Doppler Effect
Important Questions on Doppler Effect
Two engines pass blows a whistle of frequency 540Hz. Find the frequencies heard on the other engine before and after the crossing. Velocity of either engine = 30 mile/h and velocity of sound = 1144 ft/s.
A whistle is whirled in a circle of 1 m radius and traverses the circular path twice per second. An observer is situated outside the circle but in its plane. What is the interval between the highest and the lowest pitch heard if the velocity of sound be 332 m/s.
A car travelling at a speed of 36 km/h sounds its horns which have a frequency 500 Hz and this is heard in another car which is travelling behind the first car in the same direction with a velocity of 20 m/s. The sound can also be heard in the second car by reflection from a bridge ahead. What frequencies will the driver of the second car hear? Sound travels in air with a speed of 340 m/s.
Show directly without using the general formula and using neat diagrams that the frequency of sound vibrations emitted by a source will appear to be doubled to a listener fixed in space when the source approaches the listener with a speed equalling half the speed of sound.
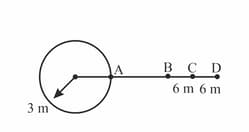
A source of sound moving along a circular orbit of radius with an angular velocity of, shown in figure below. A sound detector located far away from the source is executing linear simple harmonic motion along the line BD, with an amplitude BC = . The frequency of oscillation of the detector is. The source is at point A when the detector is at point B. If the source emits a continuous sound wave of frequency , find the maximum and minimum frequencies recorded by the detector. The speed of sound in air = .
The wavelength of yellow sodium line emitted by a star is red shifted to . What is the component of stars recessional velocity along the line of sight? (For small recessional speeds you may use a formula for Dopplers effect analogous to that for sound). Speed of light
A stationary source is an emitting sound at a fixed frequency , which is reflected by two cars approaching the source. The difference between the frequencies of sound deflected from the car is of . What is the difference in the speeds of the cars(in km per hour) to the nearest integer? The cars are moving at a constant speed much smaller than the speed of sound which is .
A whistle is revolving with a constant speed in a horizontal circle. What changes in the frequency of the whistle will appear to a person (ii) standing at the centre of the circle.
A whistle is revolving with a constant speed in a horizontal circle. What changes in the frequency of the whistle will appear to a person (i) standing outside the circle ?
Show that if the source moves away with the velocity of sound from an observer, who is at rest, the frequency of vibration is halved.
Prove that the Doppler effect is greater when the source approaches the observer than when the observer approaches the source with the same speed ?
A train is moving on a straight track with speed . It is blowing its whistle at the frequency of . The percentage change in the frequency heard by a person standing near the track of the train as the train passes him is (speed of sound ) close to
A tunning-fork of unknown frequency when sounded with another of frequency cycles per second, gives beats per second and when loaded with some wax, it is again found to give beats per second. How is it possible?
Certain characteristics' wavelength in the light form from a galaxy have larger wavelength compared to terrestrial sources. Is the galaxy approaching or receding?
Show that for light the change in the wavelength due to Doppler effect in , where the symbols have their usual meanings.
Source and the observer are moving with different velocities in different directions. How should we calculate the Doppler shift?
Explain how does velocity of wind affect Doppler shift? If there is wind but source and the observer are at rest, what would be the effect?
What is Doppler Effect? Obtain an expression for the apparent pitch of the sound heard by the listener when the listener is at rest and source of sound is moving towards the listener.?
A motorcycle starts from rest and accelerates along a straight path at . At the starting point of the motorcycle, there is a stationary electric siren. How far has the motorcycle gone when the driver hears the frequency of the siren at of its value when the motorcycle was at rest? (speed of sound = )
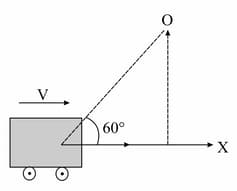
A car is moving along x-axis with a velocity . It sounds a whistle of frequency . If the speed of the sound is , the apparent frequency heard by the observer O, as shown in figure, is