First Law of Thermodynamics
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics
An ideal diatomic gas undergoes a process in which its internal energy relates to the volume as , where a is a constant. (i) find the work performed by the gas and the amount of heat to be transferred to this gas to increase its internal energy by . (ii) find the molar specific heat of the gas for this process.
An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a cylinder by a spring-located position of cross-section . Initially the gas is at and occupies a volume of and the spring is in its relaxed (unstretched, uncompressed) state. The gas is heated by a small electric small electric heater until the piston moves out slowly by . Calculate the final temperature of the gas and the heat supplied (in joules) by the heater. The force constant of the spring is , and the atmospheric pressure . The cylinder and the piston are thermally insulated. The piston is massless and there is no friction between the piston and the cylinder. Neglect heat loss through the lead wires of the heater. The heat capacity of the heater coil is negligible. Assume the spring to the massless.
One mole of an ideal gas is heated isobarically from the freezing point to the boiling point of water each under normal pressure. Find out the work done by the gas the change in its internal energy. The amount of heat involved is .
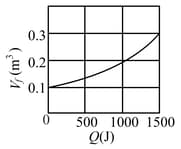
Suppose mole of an ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion as energy is added to it as heat . Graph shows the final volume versus . The temperature of the gas is :- (use and )
A gas takes part in two processes in which it is heated from the same initial state to the same final temperature. The processes are shown on the diagram by the straight line and and are the, points on the same isothermal curve. and are the heat transfer along the two processes. Then :-
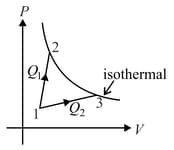
is always greater than due to the fact that :-
The internal energy of a system remains constant when it undergoes:-
When unit mass of water boils to become steam at , it absorbs amount of heat. The densities of water and steam at are and respectively, and the atmospheric pressure is . The increase in the internal energy of the water is –
An ideal gas can be expanded from an initial state to a certain volume through two different processes (i) constant and (ii) where is a positive constant. Then:-
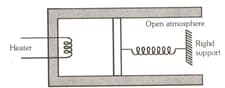
Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas are confined within a cylinder by a massless and frictionless spring-loaded piston of cross-sectional area . The spring is, initially in its relaxed state. Now the gas is heated by an electric heater, placed inside the cylinder, for some time. During this time, the gas expands and does of work in moving the piston through a distance . The temperature of the gas increases by . Calculate the spring constant and the heat supplied by the heater.
The internal energy of a gas is given by . It expands from to against a constant pressure . The heat absorbed by the gas in the process is,
Assertion: When a bottle of cold carbonated drink is opened a slight fog forms around the opening.
Reason: Adiabatic expansion of the gas causes lowering of temperature and condensation of water vapours.

