Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Periodicity, Exercise 12: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Lawrie Ryan Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Periodicity, Exercise 12: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 10: Periodicity, Exercise 12: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook with Digital Access (2 Years) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Periodicity, Exercise 12: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
The graph shows how a periodic property varies when plotted against atomic number for Period 3 (sodium to argon).
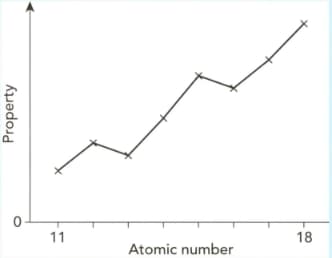
(i) Identify the property.
(ii) Explain the overall trend across the period.
i) Describe how the atomic radius varies across Periods 2 and 3.
ii) Explain this trend.
(i) Describe how the atomic radius varies down each group of the periodic table.
(ii) Explain this trend.
Describe the acid-base nature of the solutions obtained when sodium chloride is added to water. Use equations to illustrate your answer.
Describe the acid-base nature of the solutions obtained when sulphur trioxide is added to water. Use equations to illustrate your answer.
Describe the acid-base nature of the solutions obtained when sodium oxide is added to water. Use equations to illustrate your answer.
Describe the acid-base nature of the solutions obtained when phosphorus(V) chloride is added to water. Use equations to illustrate your answer.
i) Write an equation for the reaction of magnesium with cold water.
ii) Predict and explain the of the resulting solution.
