Parallel and Series Connections
Parallel and Series Connections: Overview
The topic will take you through the basics of parallel and series connections. The electric components can be added either in series—side-by-side or parallel—both arms together, giving different results.
Important Questions on Parallel and Series Connections
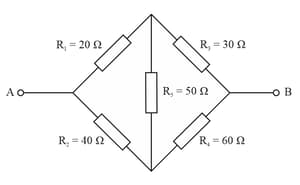
Calculate the equivalent resistance between the points and in the given figure.
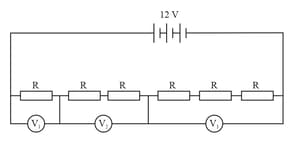
In the circuit given, what will be the readings of voltmeters , and ?
You are given a number of resistors. What is the minimum number of these resistors you will need to get a resistor?
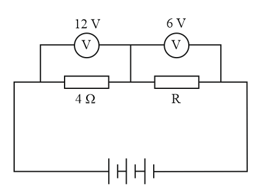
In the given circuit, calculate the potential difference across the battery, the current through the resistance and the value of the resistance .
The effective resistance when two resistors are connected in series is . If the effective resistance when the same two resistors are connected in parallel is , what are the resistances of the given resistors?
Three identical lamps are connected in parallel with a battery. The total current in the circuit is . What will be the total current in the circuit when one of the lamps fuses?
What is the smallest and the largest resistance you can produce in a circuit by combining two hundred resistors?
Two metallic wires and of same material are connected in parallel. Wire has length and radius and wire has length and radius . What is the ratio of the total resistance of parallel combination and the resistance of wire ?
Column I give the ways resistors are connected and column II gives their equivalent resistances. Match them.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) and resistors connected in parallel | (p) |
| (b) and resistors connected in parallel and then connected in series with a resistor | (q) |
| (c) and resistors connected in series and then connected in parallel to a resistor | (r) |
| (d) Ten resistors in parallel connected in series with sixteen resistors in parallel | (s) |
The equivalent resistance of two resistances, and in parallel is given by undefined. The equivalent resistance of the same two resistances in series is given by undefined.
Consider the given figure. A resistor of undefined is connected to a battery of undefined. An ammeter is connected to measure the current through the resistor and a voltmeter is connected to measure the potential difference across the same resistor. Though ideally, a voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ammeter has zero resistance, they both have finite non-zero resistances in practical situations. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the given situation have resistances of and respectively.
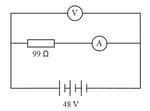
On the basis of the above information, answer the following question: What will be the current flowing through the ammeter?
The equivalent resistance of two resistances, and in parallel is given by undefined. The equivalent resistance of the same two resistances in series is given by undefined.
Consider the given figure. A resistor of undefined is connected to a battery of undefined. An ammeter is connected to measure the current through the resistor and a voltmeter is connected to measure the potential difference across the same resistor. Though ideally, a voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ammeter has zero resistance, they both have finite non-zero resistances in practical situations. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the given situation have resistances of and respectively.
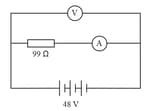
On the basis of the above information, answer the following question: What will be the current flowing through the voltmeter?
The equivalent resistance of two resistances, and in parallel is given by undefined. The equivalent resistance of the same two resistances in series is given by undefined.
Consider the given figure. A resistor of undefined is connected to a battery of undefined. An ammeter is connected to measure the current through the resistor and a voltmeter is connected to measure the potential difference across the same resistor. Though ideally, a voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ammeter has zero resistance, they both have finite non-zero resistances in practical situations. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the given situation have resistances of and respectively.
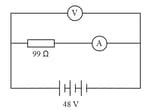
On the basis of the above information, answer the following question: What will be the current drawn from the battery when the voltmeter and the ammeter are connected?
The equivalent resistance of two resistances, and in parallel is given by undefined. The equivalent resistance of the same two resistances in series is given by undefined.
Consider the given figure. A resistor of undefined is connected to a battery of undefined. An ammeter is connected to measure the current through the resistor and a voltmeter is connected to measure the potential difference across the same resistor. Though ideally, a voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ammeter has zero resistance, they both have finite non-zero resistances in practical situations. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the given situation have resistances of and respectively.
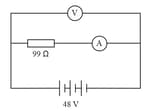
On the basis of the above information, answer the following question: What will be the total resistance of the circuit when the voltmeter and the ammeter are connected?
The equivalent resistance of two resistances, and in parallel is given by undefined. The equivalent resistance of the same two resistances in series is given by undefined.
Consider the given figure. A resistor of undefined is connected to a battery of undefined. An ammeter is connected to measure the current through the resistor and a voltmeter is connected to measure the potential difference across the same resistor. Though ideally, a voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ammeter has zero resistance, they both have finite non-zero resistances in practical situations. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the given situation have resistances of and respectively.
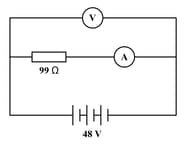
On the basis of the above information, answer the following question: What will be the current drawn from the battery when no voltmeter and ammeter are connected?
In a circuit, the potential difference across each resistance in a series combination of a number of resistances is the same as the potential difference across each resistance when the same resistances are connected in parallel.
A parallel combination of three resistors will draw more current from the battery than their series combination.
To secure maximum equivalent resistance using hundred resistors, all the resistors should be connected in parallel.
To secure minimum equivalent resistance using ten resistors, all the resistors should be connected in parallel.
The equivalent resistance of two resistors of each connected in parallel is .
A parallel combination of resistor of each is connected in series with a battery. If the current drawn from the battery is the current through each resistor will be _____.
