Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 3: Current Electricity, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course (Based on Revised Syllabus-2023) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
What is the relationship between potential difference across the terminals of a cell and emf of the cell in an open circuit?
Find the number of free electrons in a copper wire of length and cross sectional area . Determine the charge carried by these free electrons. Number density of free electrons in copper is per .
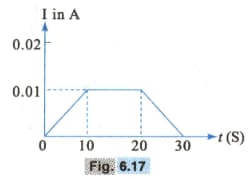
In a copper voltmeter, a varying electric current, as shown in graph of Fig. , is passed. The mass of copper deposited at the end of seconds is gram. Using this graph, find the value of electro-chemical equivalent of copper in .
Two bulbs are rated and . If they are connected in series and in parallel across a supply , find the power dissipated in the two combinations in terms of and .
A wire has resistance of ohms. It is bent to form a circle. The effective resistance between the ends of any of its diameter is
Twelve resistors each of resistance are joined to form a cube as shown in the figure given below. Find the equivalent resistance between the diagonally opposite points and .
A resistor and a resistor are connected in parallel. The combination is connected to a cell in one side and a rheostat in another side. The sliding contact of rheostat is connected to the other terminal of the battery through an ammeter. Find the maximum and minimum value of current in the circuit. Neglect the internal resistance of the cell.
A few storage cells in series are to be charged from a D.C. supply. The emf of each cell is and internal resistance . The charging current is . In this arrangement, how many cells can be changed and what extra resistance is required to be connected in the circuit?
