NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 5: LA
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 5: LA
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 12: Thermodynamics, Exercise 5: LA with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Physics - Class 11 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 5: LA with Hints & Solutions
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Figure. A to B volume is constant, B to C adiabatic, C to D: volume is constant D to A adiabatic.
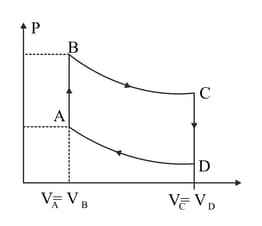
In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with
a piston) is shown in Figure.
A to B :volume constant
B to C: adiabatic
C to D: volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
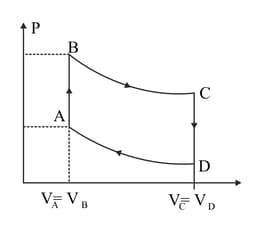
In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Figure. A to B volume is constant. B to C, the process is adiabatic, C to D volume constant
D to A is adiabatic. Also, .
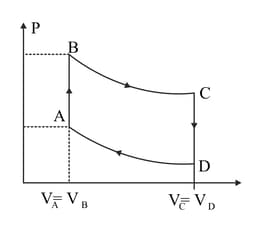
What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in terms of Given: for the gas.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in Figure.
A to B :volume constant
B to C: adiabatic
C to D: volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
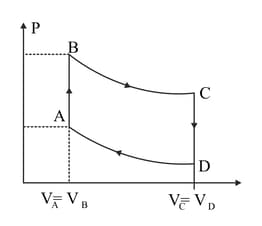
What is the efficiency of the engine?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in the figure below.
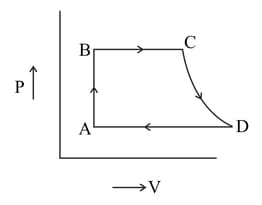
Find the heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle.
(a) AB: constant volume
(b) BC: constant pressure
(c) CD: adiabatic
(d) DA: Constant pressure
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (Figure). A spring (spring constant ) is attached (unstretched, length ) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from to .
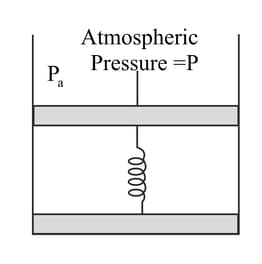
What is the initial pressure of the system?
Consider one mole of a perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross-section with a piston attached (Figure). A spring (spring constant ) is attached (unstretched length ) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and, the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from to .
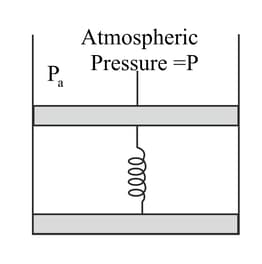
What is the final pressure of the system?
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross-section with a piston attached (Figure). A spring (spring constant ) is attached (unstretched length ) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and, the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from to .
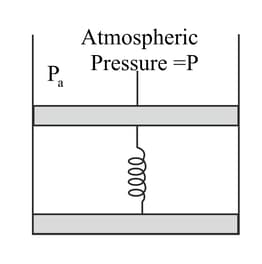
Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between and
