Second Law of Thermodynamics
Important Questions on Second Law of Thermodynamics
In a cold storage, ice melts at the rate of when the external temperature is . Find the minimum power output of the motor used to drive the refrigerator which just prevents the ice from melting. Latent heat of fusion of ice
A Carnot heat engine has an efficiency of . If the same engine is worked backward to obtain a refrigerator, then find its coefficient of performance.
In which case will the efficiency of a Carnot cycle be higher?
(a) When the temperature of the source is increased by .
(b) When the temperature of the sink is lowered by ?
The efficiency of a Carnot cycle is. By lowering the temperature of the sink, it increases too. Calculate the initial and final temperatures of the sink.
A Carnot engine is designed to operate between and . Assuming that the engine actually produces of mechanical energy per kcal of heat absorbed, compare the actual efficiency with the theoretical maximum efficiency.
A refrigerator whose coefficient of performance is , extracts heat from the cooling compartment at the rate of .
(a) How much work per cycle is required to operate the refrigerator?
(b) How much heat is discharged to the room?
A refrigerator freezes water at into ice at in a time interval of . Assuming the room temperature to be , calculate the minimum amount of power needed to make of ice
A heat engine receives of heat from the source per cycle, and operates with an efficiency of . Determine the work obtained from the engine and the heat rejected to the sink, per cycle.
During the process of an ideal gas
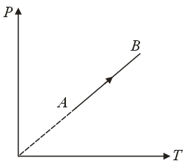
An ideal gas (, monatomic) is in the initial state (see the given figure) on an isothermal at temperature . It is brought under a constant volume process to which lies on an adiabatic intersecting the isothermal at . The change in the internal energy of the gas during the process is (in terms of )
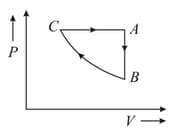
A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process shown in the given figure. It rejects of heat during the part , does not absorb or reject the heat during , and accepts of heat during . Forty joules of work is done on the gas during the part $B C$. The internal energy at point is . The internal energies at and . respectively, will be
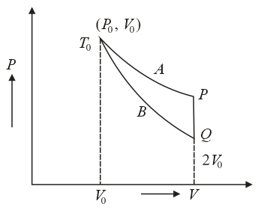
A carnot engine, whose efficiency is , takes in heat from a source maintained at a temperature of . It is desired to have an engine of efficiency . Then, the intake temperature for the same exhaust (sink) temperature must be
A carnot engine operating between temperatures and has efficiency . When is lowered by , its efficiency increases to . Then and are, respectively
A solid body of constant heat capacity is being heated by keeping it in contact with reservoirs in two ways
(i) Sequentially keeping in contact with reservoirs such that each reservoir supplies the same amount of heat.
(ii) Sequentially keeping in contact with reservoirs such that each reservoir supplies the same amount of heat.
In both the cases, the body is brought from initial temperature to final temperature . Entropy change of the body in the two cases respectively, is
A reversible engine converts one-sixth of heat absorbed at the source into work. When the temperature of the sink is reduced by , the efficiency of the engine is doubled. Find the temperatures of the source and the sink.
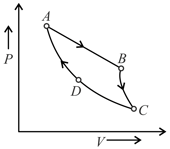
The given figure shows the diagram for a Carnot cycle. In this diagram,