MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A sample of an ideal non linear triatomic gas has a pressure and temperature taken through the cycle as shown starting from . Pressure for process is times . Calculate heat absorbed in the cycle and work done.
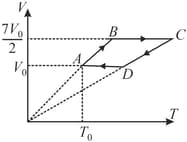


Important Questions on Thermodynamics
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
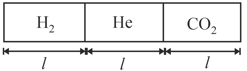
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
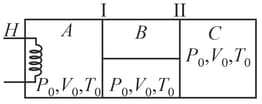
(a) Final pressures in each compartment and
(b) Final temperatures in each compartment and
(c) Heat supplied by the heater
(d) Work done by gas in and .
(e) Heat flowing across piston .
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
