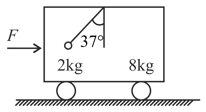
A trolley of mass is standing on a frictionless surface inside which an object of mass is suspended. A constant force starts acting on the trolley as a result of which the string stood at an angle of from the vertical (bob at rest relative to trolley). Then:


Important Questions on Laws of Motion
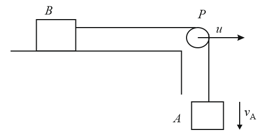
In the figure, the pulley moves to the right with a constant speed . The downward speed of is and the speed of to the right is .
In an imaginary atmosphere, the air exerts a small force on any particle in the direction of the particle’s motion. A particle of mass projected upward takes time in reaching the maximum height and in the return journey to the original point. Then
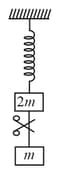
System shown in figure is in equilibrium and at rest. The spring and string are massless. Now the string is cut. The acceleration of mass and just after the string is cut will be:
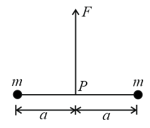
Two particles of mass each are tied at the ends of a light string of length . The whole system is kept on a frictionless horizontal surface with the string held tight so that each mass is at a distance from the centre (as shown in the figure). Now, the mid-point of the string is pulled vertically upwards with a small but constant force . As a result, the particles move towards each other on the surface. The magnitude of acceleration, when the separation between them becomes is