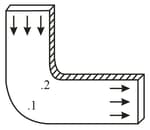
Ideal fluid flows along a flat tube of constant cross-section, located in a horizontal plane and bent, as shown in the figure. The flow is steady. Are the pressures and velocities of the fluid equal at points and ? What is the shape of the streamlines?


Important Questions on PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
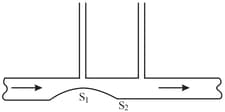
Two manometric tubes are mounted on a horizontal pipe of varying cross-section at the sections and . Find the volume of water flowing across the pipe's section per unit time, if the difference in water columns is equal to .
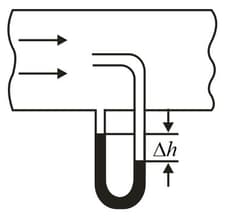
A Pitot tube is mounted along the axis of a gas pipeline whose cross-sectional area is equal to . Assuming the viscosity to be negligible, find the volume of gas flowing across the section of the pipe, per unit time, if the difference in the liquid columns is equal to , and the densities of the liquid and the gas are and , respectively.
A wide vessel with a small hole in the bottom, is filled with water and kerosene. Neglecting the viscosity, find the velocity of the water flow, if the thickness of the water layer is equal to and that of the kerosene layer is equal to
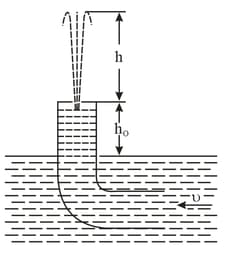
A bent tube is lowered into a water stream as shown in figure. The velocity of the stream relative to the tube is equal to The closed upper end of the tube located at the height has a small orifice. To what height will the water jet spurt?
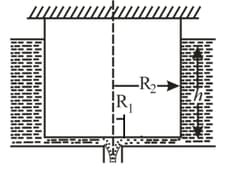
The horizontal bottom of a wide vessel with an ideal fluid has a round orifice of radius over which a round closed cylinder is mounted, whose radius . The clearance between the cylinder and the bottom of the vessel is very small, the fluid density is Find the static pressure of the fluid in the clearance as a function of the distance from the axis of the orifice (and the cylinder), if the height of the fluid is equal to
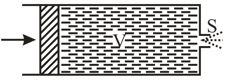
What work should be done in order to squeeze all water from a horizontally located cylinder during the time by means of a constant force acting on the piston? The volume of water in the cylinder is equal to the cross-sectional area of the orifice to with being considerably less than the piston area.The friction and viscosity are negligibly small.
A cylindrical vessel of height and base area is filled with water. An orifice of area is opened in the bottom of the vessel. Neglecting the viscosity of water, determine how soon all the water will pour out of the vessel.
