EASY
Earn 100
On increasing the potential difference between anode and cathode the photoelectric current :-
(a)increases
(b)first increases then decreases
(c)first increases then becomes constant
(d)decreases
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
HARD
HARD
EASY
EASY
The following graph represents the variation of photo current with anode potential for a metal surface. Here and represents intensities and represents frequency for curves and respectively, then
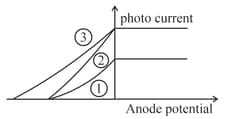
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
The photoelectric threshold for a certain metal surface is . If the metal surface is irradiated by a wavelength of , the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Given figure shows few data points in a photo-electric effect experiment for a certain metal. The minimum energy for ejection of electrons from its surface is: (Planck's constant )
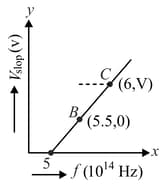
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM

