Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives
Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids, Colour and Odour of Carboxylic Acids, Boiling Points of Carboxylic Acids, Melting Points of Carboxylic Acids, Solubility of Carboxylic Acids in Water, etc.
Important Questions on Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives
The physical state of pure acetic acid at is
In vapour phase, acetic acid exists as
Most of the carboxylic acid undergo dimerisation in organic solvent due to:
Which of the given compounds has the highest boiling point?
Which of the following compounds has highest boiling point?
What sized ring is formed when two carboxylic acids form a dimeric structure through inter- molecular hydrogen bonding? (consider hydrogen bond as a bond)
What is the odour of Carboxylic Acids with more than 9 carbon atoms?
Which of the following is the key ingredient in vinegar?
Many carboxylic acids are _____ liquids with disagreeable odors.
Carboxylic acids have locker room odour.
Decreasing order of melting point of compound to follows:
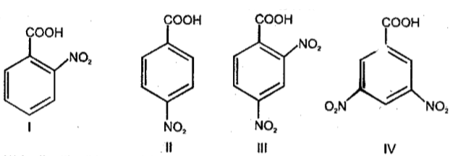
Decreasing order of boiling point of to follow:
Correct water solubility order/s amongst the following pairs is/are:
The molecular weight of benzoic acid in benzene as determined by depression in freezing point method corresponds to :
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds
(I)
(II)
(III)
The boiling point of ethyl alcohol should be less than that of
State the oxidation number of carbonyl carbon in methanal and methanoic acid respectively.
Choose the incorrect statement
Which of the following statement is correct?
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds
(l) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
(ll) CH3CH2CH2CHO
(lll) CH3CH2CH2 COOH
