Chemical Reactions of Haloalkanes
Chemical Reactions of Haloalkanes: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Chemical Reactions of Haloalkanes, Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Alkyl Halides, Ambident Nucleophiles & Grignard Reagent etc.
Important Questions on Chemical Reactions of Haloalkanes
and reactions differ from each other because of
Identify A, B, C and D in the following process :
(i)
(ii)
What is the order of reactivity of following compounds towards substitutions reaction.
(i) 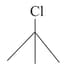
(ii) 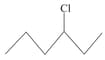
(iii) 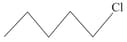
What is the order of reactivity of following compounds towards substitution reaction.
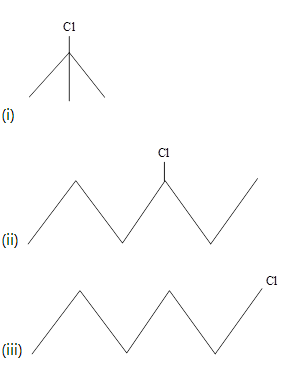
Which one of the following two substances undergoes reaction faster?
(i) 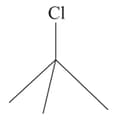 or (ii)
or (ii) 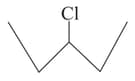
An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives:
A solution of (+) -2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of small amount of , due to the formation of –
A solution of (+) -2-chloro-1-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of small amount of , due to the formation of:
on treatment with produces –
on treatment with produces:
1–chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives –
n–Propyl bromide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide produces –
The major product of the following reaction is
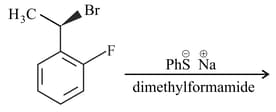
The product of following reaction is –
In the reaction,
The product C is.
In the following question a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion: reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide.
Reason: is an ambident nucleophile.
Match the alkyl halide reacting with reagent given in Column with their respective substituted product given in Column and choose the correct option from the codes given below:
|
Column |
Column |
Discuss how alkyl cyanides and alkyl nitrites are formed.
Define ambident nucleophiles? Give an example of it.
Which of the given options shows the correct product of the reaction,
