Redox Reactions and Titration
Redox Reactions and Titration: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Redox Reactions as a Basis for Titrations etc.
Important Questions on Redox Reactions and Titration
acts as an oxidising agent in alkaline medium. When alkaline is treated with , iodide ion is oxidised to . The value of is _____.
How many of must be reacted with of if the redox products are and
of household bleach solution was mixed with of and of acetic acid. In the titration of the liberated iodine, of was used to reach the end point. The molarity of the household bleach solution is
of nitric acid, of hydrochloric acid and a certain volume of sulphuric acid are mixed together and made up to . of this acid mixture exactly neutralise of sodium carbonate solution containing one gram of in of water. Calculate the amount in grams of the sulphate ions in solution. Report the answer after multiplying with 10 and round off to the nearest integer.
Conductometric titration curve of an equimolar mixture of HCl and HCN with NaOH (aq) is
solution on treatment with KI and titration of liberated I2, required hypo. Thus H2O2 is -
Acidified oxidises oxalic acid to What is the volume (in litres) of required to completely oxidise of oxalic acid in acid medium?
Amount of oxalic acid present in a solution can be determined by its titration with solution in the presence of The titration given unsatisfactory result when carried out in the presence of HCl because HCl
The oxidation state of chromium in the final product formed by the reaction between KI and acidified potassium dichromate solution is
A mixture of and is completely reacted with of acidified solution. The resultant solution was then titrated with zinc dust which converted of the solution to . The required of solution. Find out the percentage weight of in the mixture.
1.2 g of a salt with its empirical formula KxHy(C2O4)z was dissolved in 50 mL of water and its 10 mL portion required 11 mL of a 0.1 M HCl solution to reach the equivalence point. In a separate titration, 15 mL of the stock solution required 20 mL 0.2475 M KOH to reach the equivalence point. Determine the empirical formula of salt.
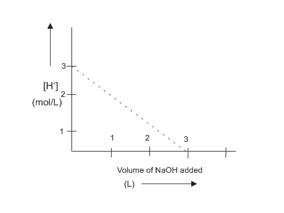
1 M NaOH solution was slowly added into 1000 mL of 183.75 g impure H2SO4 solution and the following plot was obtained. The percentage purity of H2SO4 sample and slope of the curve respectively are :