Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions
Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Enthalpy of Dilution, Lattice Enthalpy, Kirchhoff's Equation at Constant Pressure & Kirchhoff's Equation at Constant Volume etc.
Important Questions on Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions
From the data of following bond energies:
Calculate the enthalpy of the following reaction in .
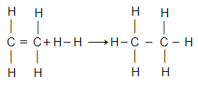
Given that bond energies of respectively and for , bond enthalpy of is:
For which one of the following equations is equal to for the product?
What is the enthalpy change for,
if heat of formation of are and respectively (in standard conditions)?
The values of heat of formation of are –298.2 kJ and –98.2 kJ. The enthalpy change of the reaction
will be
Assume each reaction is carried out in an open container. For which reaction will
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction:
will be:
[Consider the actual value instead of magnitude].
For the reaction:
at constant temperature, is:
Which one of the following is the correct relation between and for one mole of an ideal gas? ( is molar gas constant)
The standard enthalpy of formation of and are , and respectively. The amount of heat liberated (in ) when of methane gas is burnt under standard conditions is
of a mixture of acetylene and ethane produced on combustion, of heat energy. The enthalpies of combustion of acetylene and ethane are and respectively. The ratio of acetylene to ethane in the mixture is
How many of the following have standard heat of formation value of zero.
In Kirchhoff's equation, the term is used instead of at constant volume.
Kirchhoff's equation at constant volume is :
The variation of with temperature is expressed by Kirchoff's equation.
Temperature affects the enthalpy change of a reaction.
Write the Kirchhoff's equation at constant volume and at constant pressure.
Specific heat capacity is not the parameter that is used to relate the enthalpy of a reaction and temperature.
Describe the effect of temperature on enthalpy of reaction.
What happens to the enthalpy of the system if its temperature increases?
