Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity
Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Average Velocity of Electron in the Absence of Electric Field, Acceleration of Electron in an Electric Field, Conductivity & Mobility of Electron etc.
Important Questions on Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity
Two conducting wires X and Y of same diameter but different materials are joined in series across a battery. If the number density of electrons in X is twice that in Y, find the ratio of drift velocity of electrons in the two wires would be:
The current of a conductor flowing through a conductor in terms of the drift speed of electrons is (the symbols have their usual meanings)
Derive an expression for the resistivity of a good conductor, in terms of the relaxation time of electrons.
The number density of free electrons in a copper conductor is How long does an electron take drift from one end of a wire 3.0 m long to its other end? The area of cross-section of the wire is and is carrying a current of 3.0 A.
The number density of free electrons in a copper conductor is estimated at How long does an electron take to drift from one end of a wire 3.0 m long to its other end? The area of cross-section of the wire is and it is carrying a current of 3.0 A.
The relation between current and drift velocity is
Relation between drift velocity of electron and thermal velocity of electron at room temp is expressed as
The current in a copper wire is increased by increasing the potential difference between its ends. Which one of the following statements regarding the number of charge carriers per unit volume in the wire and , the drift velocity of the charge carriers is correct?
Assertion
A current flows in a conductor only when there is an electric field within the conductor.
Reason
The drift velocity of electron in presence of electric field decreases.
Assertion: If an electron and proton enter an electric field with equal energy, then path of electron is more curved than that of proton.
Reason: Electron has a tendency to form curve.
In the uniform electric field of , an electron is accelerated from rest. The acceleration of the electron is nearly (Charge of electron )
When potential difference across a given copper wire is increase, drift velocity of charge carriers
Two rods of copper and iron with the same cross sectional area are joined at and a steady current flows through the rods as shown in the figure.
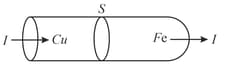
Choose the most appropriate representation of charges accumulated near the junction .
The resultant flow of current in a conductor in the absence of electric field is
The resultant flow of current in a conductor in the absence of electric field is
A current is flowing through the wire of diameter having drift velocity of electrons in it. What will be new drift velocity when diameter of wire is made
When temperature of a metal is increased, its conductivity
Conductivity of the metal is
A metal wire carries a charge of in minutes. If the area of the cross-section of the wire is and the material of the metal contains free electrons , the drift velocity of the electrons in the wire is
Which of the following statements is true about relaxation time?
