Potential Due to a Point Charge
Potential Due to a Point Charge: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electric Potential due to a Point Charge at a Point, Graph of Electric Field Due to Point Charge, and Graph of Electric Potential Due to Point Charge.
Important Questions on Potential Due to a Point Charge
Electric potential due to point charge in air is expressed as as . i.e for to potential varies
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be symmetric
Electric potential due to point charge in air is expressed as as . i.e for to potential varies
Which of the follow graph is correct for potential due to point charge at any point versus distance as shown in figure.
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be _____ symmetric
A metallic sphere A isolated from the ground is charged to . This sphere is brought in contact with other isolated metallics sphere B of half the radius of sphere A. The charge on the two sphere will now be in the ratio
What is the electric potential at a point distance from a point charge of coulomb? Round it to the nearest integer.
The potential at a point due to a charge of located away is (Assume )
An electric charge is placed at the origin. Two points and are situated at and respectively. The potential difference between the points and will be
The electric potential due to a point charge at some point in free space is . If the entire system is now placed in a dielectric medium of dielectric constant . What will be the potential at the same point in volt?
Show that the electric potential due to a point charge when surrounded by some dielectric medium is times of the electric potential when the charge is in free space.
A charge of is located at the origin of coordinate system. The potential difference between points and is
The electric potential is at a distance of from a point charge Then, is equal to
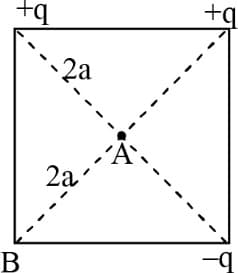
If three point charges are placed at the three corners of a square of diagonals as shown in the figure. Then, will be
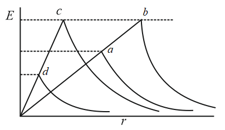
There are four sphere of each with radius as ,, , , each sphere is solid, insulating and uniformly charged. Variation of electric field with distance from the centre is given. Straight portion of curve and is overlapping and straight portion of curve and is overlapping.
Four charges of , , and are placed at the corners of a square of side . The square is in plane and its center at its origin. Electric potential due to these charges is zero everywhere on the line -
Two equal point charges are fixed at and , on the -axis. Another point charge is placed at the origin. The change in the electrical potential energy of , when it is displaced by a small distance , along -axis, is approximately proportional to
A square of side has charge at its centre and charge at one of the corners. The work required to be done in moving the charge from the corner to the diagonally opposite corner is
An electric charge is placed at the origin of coordinate system. Two points and are situated at and respectively. The potential difference between the points and will be,
Two charges, and , are kept apart. Then, at any point on the right bisector of line joining the two charges,