Electric Potential Due to a Point Charge and Dipole
Electric Potential Due to a Point Charge and Dipole: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Potential Due to Dipole at Axial Point, Graph of Electric Potential Due to Point Charge, Electric Potential due to Two or More Charges at a Point & Graph of Electric Potential Due to Two Point Charges etc.
Important Questions on Electric Potential Due to a Point Charge and Dipole
Two point charges are separated by a distance of 1m in air. Calculate at what point on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero.
Electric potential due to point charge in air is expressed as as . i.e for to potential varies
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be symmetric
Electric potential due to point charge in air is expressed as as . i.e for to potential varies
Which of the follow graph is correct for potential due to point charge at any point versus distance as shown in figure.
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be _____ symmetric
A metallic sphere A isolated from the ground is charged to . This sphere is brought in contact with other isolated metallics sphere B of half the radius of sphere A. The charge on the two sphere will now be in the ratio
What is the electric potential at a point distance from a point charge of coulomb? Round it to the nearest integer.
The potential at a point due to a charge of located away is (Assume )
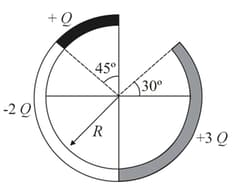
Figure shows three charged circular arcs, each of radius their centres are at same point and total charge as indicated. The net electric potential at the centre of curvature :-
An electric charge is placed at the origin. Two points and are situated at and respectively. The potential difference between the points and will be
The electric potential due to a point charge at some point in free space is . If the entire system is now placed in a dielectric medium of dielectric constant . What will be the potential at the same point in volt?
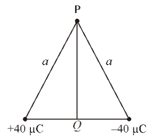
For the arrangement of charges as shown in adjoining diagram, the work done in moving a charge from to (in joule) is
A charge of is located at the origin of coordinate system. The potential difference between points and is
In a hydrogen atom, the electron revolves around the nucleus in an orbit of radius . Then the electrical potential produced by the nucleus at the position of the electron is
The electric potential is at a distance of from a point charge Then, is equal to
Two electric dipoles and are at points and separate by distance Find the distance from point where net electric potential is zero.
Consider a spherical shell of radius with a total charge uniformly spread on its surface (center of the shell lies at the origin ). Two point charge, are brought, one after the other, from far away and placed at respectively. Magnitude of the work done in this process is
Assertion: When two charges are brought close to each other, potential energy of the system may increase or decrease.
Reason: When work done by a conservative force is positive, the potential energy of the system increases, and when work done by a conservative force is negative, the potential energy of the system decreases.
Assertion: The work done by a non-uniform electric field on a charged particle starting from rest may be zero. (Assume no other forces act on the charged particle).
Reason: The angle between electrostatic force and velocity of the charged particle released from rest in non-uniform electric field is always acute. (Assume no other forces act on the charged particle.)
