Laws of Friction
Laws of Friction: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Laws of Friction, Graph of Frictional Force, Laws of Static Friction, Laws of kinetic friction, Cause of friction, Limiting friction.
Important Questions on Laws of Friction
A force is applied parallel to the plane on an ice on a frictional horizontal plane, the acceleration-force graph is as shown in the figure.
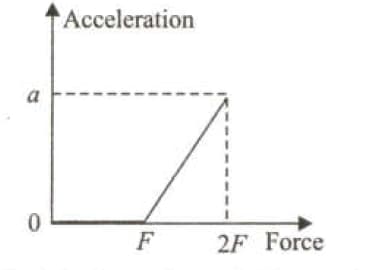
If half of the ice melts and falls on the ground, which of the following would be the acceleration versus force graph?
Which of the following statements about friction is true?
What is Static Friction?
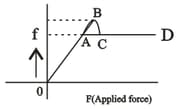
Graph of frictional force :-
(i) From the graph of frictional force versus applied force if static and kinetic frictional forces are represented by then.
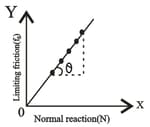
In the given limiting frictional force vs normal reaction graph which of the following is measured by the slope of the graph.
In the graph of frictional force vs applied force for a box kept on the rough surface such that box is about to move then
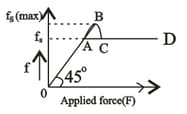
In the graph of frictional force vs applied force, what should be the slope so that static frictional force is adjusted to applied force.
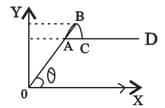
The variation of frictional force with respect to applied force is given in figure.
Which part of the graph represents kinetic friction.
Why is it much easier to balance a meter scale on your fingertip than balancing on a match stick?
Why does a porter bend forward while carrying a sack of rice on his back?
A body takes n times as much time to slide down a rough incline as it takes to slide down a smooth incline. The coefficient of friction between the body and the incline will be
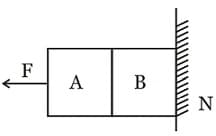
Given in the figure are two blocks A and B of weight 20N and 100N, respectively. These are being pressed against a wall by a force F as shown. If the coefficient of friction between the blocks is 0.1 and between block B and the wall is 0.15, the frictional force applied by the wall on block B is:
A block is gently placed on a conveyor belt moving horizontally with constant speed. After 4s the velocity of the block becomes equal to the velocity of belt. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the belt is 0.2, then velocity of the conveyor belt is
A block of mass kg resting on a horizontal surface. A force is applied on the block as shown in figure. If coefficient of friction between the block be , what can be the maximum value of force so that block does not start moving? (Take )
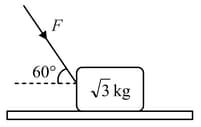
A block of mass is placed on the floor. The coefficient of static friction is, a force of is applied on the block as shown in the figure. The force of friction between the block and the floor is
(Take )
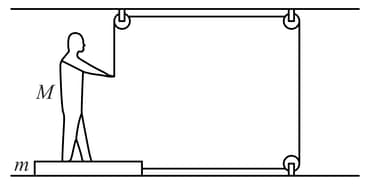
The friction coefficient between the board and the floor shown in diagram is . Find the maximum force that the man can exert on the rope, so that the board does not slip on the floor.