Intuitive Concepts of Force and Inertia
Intuitive Concepts of Force and Inertia: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Aristotle Fallacy, Properties of Force, Cutting of Springs in a Ratio & Effect of Cutting of Springs and Strings in System etc.
Important Questions on Intuitive Concepts of Force and Inertia
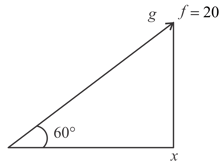
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block (g is acceleration due to gravity) will be
A monkey of mass is holding a vertical rope. The rope will not break when a mass of is suspended from it but will break if the mass exceeds . What is the maximum acceleration with which the monkey can climb up along the rope?
A man weighing 80 kg, stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform acceleration of What would be the reading on the scale?
If a cricketer catches a ball of mass moving with a velocity of , then he experiences a force of (Time taken to complete the catch is )
A monkey is descending from the branch of a tree with constant acceleration. If the breaking strength is 75% of the weight of the monkey, the minimum acceleration with which monkey can slide down without breaking the branch is
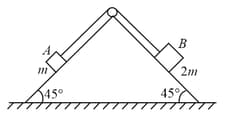
Block of mass and block of mass are placed on a fixed triangular wedge by means of a massless inextensible string and a frictionless pulley as shown in figure. The wedge is inclined at to the horizontal on both sides. The coefficient of friction between block and the wedge is and that between block and the wedge is . If the system of and is released from rest, find the magnitude and direction of the force of friction acting on
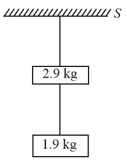
Two blocks of mass and are suspended from a rigid support by two inextensible wires each of length see figure. The upper wire has negligible mass and the lower wire has a uniform mass of . The whole system of blocks, wires and support has an upward acceleration of . Acceleration due to gravity is .
(i) Find the tension at the mid-point of the lower wire.
(ii) Find the tension at the mid-point of the upper wire.
A spring balance is attached to the ceiling of a lift. A man hangs his bag on the spring and the spring reads when the lift is stationary. If the lift moves downward with an acceleration of , the reading of the spring balance will be,
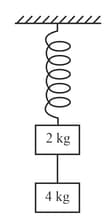
A mass is attached to two springs as shown in figure. The spring constants of two springs are and For the frictionless surface, the time period of oscillation of mass is
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A : An electric fan continues to rotate for some time after the current is switched off.
Reason R: Fan continues to rotate due to inertia of motion.
In the light of above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
A body of mass is in equilibrium due to forces and . and are perpendicular to each other. If is removed then find the acceleration of body. Given and .
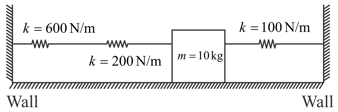
For the situation shown in the figure, horizontal spring and the spring connecting blocks and are light. The blocks and are of same mass . The pulley is smooth and fixed. The accelerations of and just after cutting the horizontal spring are
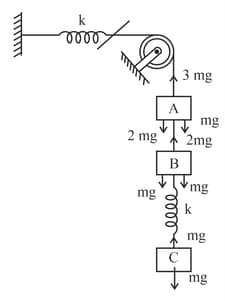
The system shown in figure is in equilibrium initially. String connecting blocks is cut at . Magnitude of the relative acceleration of blocks (in ) just after the string is cut is
The force required to stretch a spring varies with the distance as shown in the figure. If the experiment is performed with the above spring of half the length, the line will:
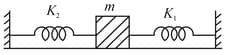
A mass is stationary in the position shown. Each of the three springs are relaxed. Each spring has a characteristic stiffness constant , as shown on the diagram. If the mass is now displaced to the right, what will be the net force, in newtons, exerted by the three springs on the mass? Ignore gravity

The force exerted by a special compression device is given as function of compression as for , where is the maximum possible compression and is a constant. The force exerted by the device under compression is maximum when compression is:
In the given diagram system is in equilibrium. If applied force is doubled how much distance, the mass less block will more towards right before new equilibrium is achieved.
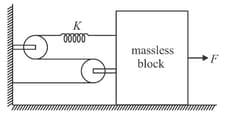
If a spring of stiffness '' is cut into two parts '' and '' of length , then the stiffness of spring '' is given by:
Two blocks and of equal mass are arranged as shown with springs and . Spring is pulled with force . Acceleration of block is towards right at an instant. If is suddenly removed at this instant, the instantaneous acceleration of and will be (assume no friction)
A box is pulled with force of at angle of above the horizontal. Then the horizontal and vertical components of the force are