Potential Energy and its Types
Potential Energy and its Types: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Work Done by Spring Force, Potential Energy, Force and Potential Energy, Energy Stored in Spring, and Gravitational Potential Energy and mgh.
Important Questions on Potential Energy and its Types
The energy of a body due to its position or change in shape is known as _____energy.
Formula for potential energy is_____.
Water stored in a dam posseses
A body is falling from a height h. After it has fallen a height h/2, it will possess_____.
Water stored in a dam possesses_____.
A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In this process the potential energy of the car_____.
The energy possessed by a body due to its position is called
If mass of an object, m = 10 kg, displacement (height) h = 6m, and acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 ms-2. Then potential energy is
In a uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T a short bar magnet of magnetic moment m = 0.32 J/T is placed. What is the potential energy of the magnet in unstable position , if the bar is free to rotate in the plane of the field?
In the arrangements shown below, all the balls are identical and strings are light. There is no friction. In each of the three arrangements and , the system is in equilibrium.
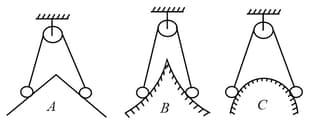
The hill slopes are identical on the two slides in each of the arrangements.
One of the balls in each arrangement is pulled down a little along the hill slope.
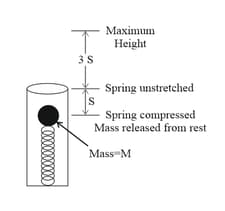
A spring-loaded toy gun is used to shoot a ball of mass M straight up in the air. The ball is not attached to the spring. The ball is pushed down onto the spring so that the spring is compressed a distance S below its un-stretched point. After release, the ball reaches a maximum height 3S, measured from the un-stretched position of the spring (see diagram). The spring constant of the spring is:-
Two wires are stretched through same distance. The force constant of second wire is half as that of the first wire. The ratio of work done to stretch first wire and second wire will be
A block of mass 0.18 kg is attached to a spring of force constant . The coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is 0.1. Initially the block is at rest and the spring is unstretched. An impulse is given to the block.
The block slides a distance of 0.06m and comes to rest for the first time the initial velocity of the block in is . Then N is
A particle which is constrained to move along the -axis, is subjected to a force in the same direction which varies with the distance of the particle from the origin is . Here, and a are positive constants. For the functional from of the potential energy of the particle is
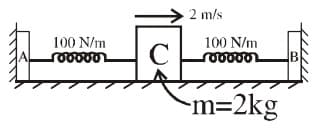
and are massless supports attached to two springs, both the springs are identical and light. Friction coefficient between block and horizontal surface is . When both the springs are in their natural length block was given a velocity of towards right. Then the distance travelled by block before coming to rest for the first time is :
A balloon is rising from the surface of earth. Then its potential energy
The block of mass moving on the frictionless horizontal surface collides with the spring of spring constant and compresses it by length . The maximum momentum of the block after collision is
A freely falling body takes to reach the ground. One second after release, the percentage of its potential energy, that is still retained is
A rubber ball falling from a height of rebounds from a hard floor to a height of . The loss of energy during the impact is
The elastic potential energy of a stretched spring is given by where is the displacement in meter and is in joule, then the force constant of the spring is
