Doppler Effect
Doppler Effect: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Doppler's Effect in Sound, Real and Apparent Frequencies in Doppler Effect, Real and Apparent Wavelengths in Doppler Effect, and Source Moving Away from Stationary Observer in Doppler Effect.
Important Questions on Doppler Effect
An observer moves towards a stationary source of sound with a velocity one-fifth of the velocity of sound. The percentage change in the apparent frequency is
A passenger sitting in a moving train records a frequency of while the train approaches the siren. During his return journey in a different train , he records a frequency of while approaching the same siren. Given siren placed at a railway platform is emitting sound of frequency . Find the ratio of velocity of train to that of train .
A bus is moving with a velocity of towards a huge wall. The driver sounds a horn of frequency . If the speed of sound in air is , Calculate the number of beats heard per second by a passenger on the bus. Take speed of sound .
Two tuning forks and lying on opposite sides of observer and of natural frequency move with velocity relative to a stationary observer . Fork moves away from the observer while the fork moves towards him. Wind with a speed is blowing in the direction of motion of fork . Find the beat frequency measured by the observer in . (Take speed of sound in air as )
When the source and the listener move in the same direction with a speed equal to the half of the speed of sound, the change in frequency of the sound is
Two cars moving in opposite directions approach each other with speed of and respectively. The driver of the first car blows a horn having a frequency . The frequency heard by the driver of the second car is [velocity of sound ]
Doppler shift :-
In case of doppler shift what will happen with the wavelength when both move away from each other.
Doppler shift :-
A source of sound is moving towards the observer then in Doppler shift wavelength ?
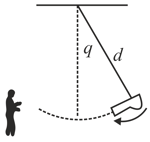
A source on a swing which is covering an angle from the vertical is producing a frequency The source is distant from the place of support of the swing. If velocity of sound is , acceleration due to gravity is , then the maximum and minimum frequency heard by a listener in front of swing is
A source of sound emitting waves of frequency and an observor are located at some distance from each other. The source is moving with a speed of at an angle of with the source observer line as shown in the figure. The observer is at rest. The apparent frequency observer by the observer (velocity of sound in air ) is:
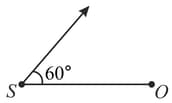
Policemen buzz a whistle frequency . A car driver is approaching the policemen. The speed of a car is Find out the change in frequency experienced by the driver when a driver approaches the policemen, and after he crosses the policemen? [Velocity of sound is.
Assertion: Motion of source with respect to the stationary observer is not equivalent to the motion of an observer with respect to a stationary source.
Reason: Doppler formula for a sound waves is symmetric with respect to the speed of the source and speed of the observer.
Two sources are at a finite distance apart. They emit sounds of wavelength . An observer situated between them on the line joining approaches one source with speed . Then the number of beats heard by observer will be :
When an engine passes near to a stationary observer then its apparent frequencies occurs in the ratio . If the velocity of sound is then the speed of the engine is
Source and observer both start moving simultaneously from the origin, one along axis and the other along axis with a speed of source equal to twice the speed of the observer. The graph between the apparent frequency observed by observer and time would be: ( is the frequency of the source)
As the train crosses a stationary observer, the apparent change in frequency of sound is in the ratio If the velocity of sound in air is , the velocity of train is
A source and observer are approaching each other with velocity. What will be the original frequency if the observer receives cycles per second?
A source is approaching a stationary observer with velocity that of sound. The ratio of observed and real frequencies will be:
A small source of sound moves on a circle as shown in the figure and an observer is sitting at . Let at be the frequencies heard when the source is at , and respectively.
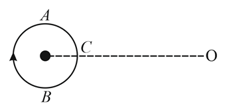
An observer starts moving with uniform acceleration, towards a stationary sound source of frequency. As the observer approaches the source, the apparent frequency(f) heard by the observer varies with time () is
