The Human Eye
Important Questions on The Human Eye
Which part of the eye controls the size of the pupil?
Which eye is likely to be in the brightest light?
Which of the following correctly gives the sequence of events that take place when human eye changes its focus from a distant object to an object closer to the eye?
The iris is a muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil. It consists of two layers: the front pigmented fibrovascular layer known as a stroma and, beneath the stroma, pigmented epithelial cells. The colour of the eye is defined by the pigmentation of the iris.
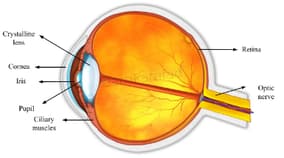
Which of the following can be directly affected if the iris does not function properly?
The far point and the near point refer to the visibility of objects close by and far away from the human eye respectively. These are the maximum and minimum distances at which an object is clearly visible to a person.
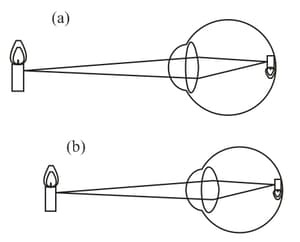
The near point and the far point are determined with regard to the function of which part of the eye?
What would the size of the image formed on the retina depend on?
What type of image is formed on the retina?
Which part of the eye produces maximum refraction of light rays?
The diagram shows how a human eye sees a candle.
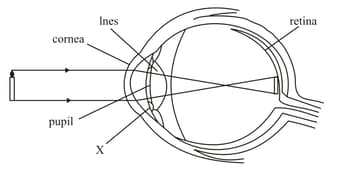
What is X?
A lens of focal length is being used by Debashree in the laboratory as a magnifying glass. Her least distance of distinct vision is .
(i) What is the magnification obtained by using the glass?
(ii) She keeps a book at a distance from her eyes and tries to read. She is unable to read. What is the reason for this?
Hypermetropia and myopia are the most common defects of vision affecting humans. Both these defects can be corrected and perfect vision can be restored with the use of suitable lenses of appropriate focal lengths. Hypermetropia can be corrected by using convex lenses while myopia can be corrected by using concave lenses. The power of prescribed lens for both these defects depends on the focal length of the respective corrective lens. The power, of the lens is given by
Now, consider a situation in which the near point of a defective eye is at a distance of . Assuming the near point of a normal eye to be , answer the following question:
If one wishes to reduce the near point of this eye to by using a lens, what will be its power?
A defective eye cannot see distinctly the object beyond clearly. What is the defect? What is the power of the lens required to rectify the defect?
Differentiate the eye defects: Myopia and Hypermetropia.
Define power of accommodation of human eye and calculate its value for a normal human eye.
If Ram, a myopic person uses spectacles of power then what will be the distance of far point of his eye?
The far point of a myopic person is in front of the eye. Calculate the focal length and power of a lens required to enable him to see distant objects clearly.
Draw a neat diagram of the human eye and indicate its main parts.
How would you calculate the power of the concave lens to correct myopia?
How would you calculate the power of the convex lens to correct hypermetropia?
Differentiate between myopia and hypermetropia.

