Elastic Collision
Elastic Collision: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Coefficient of Restitution, Cases in Expressions of Velocities for Elastic Collisions and, Linear Impulse and Coefficient of Restitution
Important Questions on Elastic Collision
Two identical balls each of mass moving on straight track are approaching towards each other with same speed. Final kinetic energy of the two ball system is equal to the total energy loss during collision. is the total kinetic energy of the balls before collision and is after collision and coefficient of restitution is . Then choose the correct options
When both billiard balls collide inelastically, the coefficient of restitution (e) will be
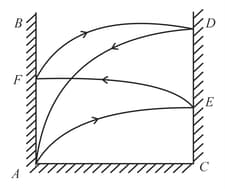
A particle is projected from the foot of one wall towards other parallel wall as shown in figure. After various collisions, finally after striking at point normally it comes back directly to the point of projection. If is the coefficient of restitution for each impact then is equal to
A ball released from a height of , hits the ground and rebound to a height of . The coefficient of restitution of the collision will be
A ball falls from a height such that it strikes the floor of lift at . If lift is moving in the upward direction with a velocity , then velocity with which the ball rebounds after elastic collision will be
A cricket ball is dropped from a building of height and the coefficient of restitution between the ground and ball is . The total distance covered by the ball before it comes to rest is
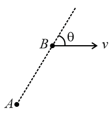
Particle is at rest and particle is moving with constant velocity as shown in diagram at . Find their velocity of separation.
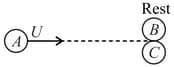
A sphere of mass moving with velocity collides head on elastically with a sphere of mass at rest. After collision their respective velocities are and . The value of :
Two identical masses are kept in contact on a smooth horizontal surface as shown. A third identical mass moving with speed hits the two balls symmetrically and comes to rest. The coefficient of restitution is
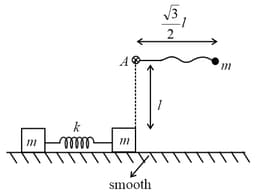
A simple pendulum of length and mass is hinged at point in a vertical plane as shown in the figure. The ball is released from the same horizontal level at a distance from point . At the lowest point bob hits a block of identical mass elastically. The maximum compression in the spring is meter. Find the value of .
(take , and ground is smooth)
A ball is dropped from height . After striking the ground time it rebounds to height . Then coefficient of restitution is
A ball is dropped from height above floor. Ball continuously bounces on the floor. Find speed just after second bounce if coefficient of restitution is :-
A smooth sphere of mass moving with horizontal speed strikes at right angles a vertical wall and bounces off the wall with horizontal speed . The coefficient of restitution between the sphere and the wall and the impulses exerted on the wall at impact.
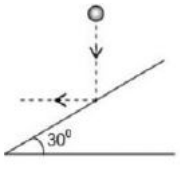
A ball is released from a point, it goes vertically downwards and collides with a fixed smooth inclined plane of angle of inclination of . After the collision the ball goes horizontally. The coefficient of restitution between the ball and the inclined plane is
In the figure shown, mass is moving with velocity and all after masses are stationary. All collisions are elastic. To transfer maximum velocity to , all masses should have their values in 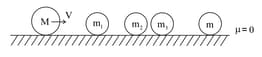
If two bodies of equal masses collide elastically, then.
Write the relation between linear impulse and coefficient of restitution.
What is the ratio of the final to initial relative speed between two objects after they collide known as:
In case of inelastic collision, the coefficient of restitution is one.
The coefficient of restitution gives us information about the collision's elasticity.
