Doppler Effect in Sound
Doppler Effect in Sound: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Doppler Shifts, Doppler's Effect in Sound, Doppler Effect when Both Source and Observer Moving with Different Velocities and, Observer Moving towards a Stationary Source in Doppler Effect
Important Questions on Doppler Effect in Sound
A radar operates at wavelength . If the beat frequency between the transmitted signal and the signal reflected from aircraft is , then velocity(in ) of the aircraft will be
A bus is moving with a velocity of towards a huge wall. The driver sounds a horn of frequency . If the speed of sound in air is , Calculate the number of beats heard per second by a passenger on the bus. Take speed of sound .
Two tuning forks and lying on opposite sides of observer and of natural frequency move with velocity relative to a stationary observer . Fork moves away from the observer while the fork moves towards him. Wind with a speed is blowing in the direction of motion of fork . Find the beat frequency measured by the observer in . (Take speed of sound in air as )
Doppler effect of sound depends on relative velocity between source and observer,
The wavelength of a sound wave emitted from a stationary source is . If the source starts moving with a velocity of towards a stationary observer, then what will be the wavelength (in ) of the sound wave (rounded off to the nearest integer) reaching the observer? [velocity of sound ]
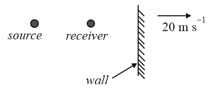
A source of sound having frequency and a receiver are located along the same line normal to the wall as shown in the figure. Both the source and the receiver are stationary and the wall recedes from the source with a velocity of . If the beat frequency registered by the receiver is , then what is the value of ? [velocity of sound = ]
Two cars are approaching each other at an equal speed of When they see each other, both blow horns having frequency of The beat frequency heard by each driver will be _________ [Velocity of sound in air is ]
An observer starts moving with uniform acceleration, towards a stationary sound source of frequency. As the observer approaches the source, the apparent frequency(f) heard by the observer varies with time () is
Two cars moving in opposite directions approach each other with speed of and respectively. The driver of the first car blows a horn having a frequency The frequency heard by the driver of the second car is [velocity of sound ]
The driver of car travelling with speed 30 m/sec towards a hill sounds a horn of frequency 600 Hz. If the velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s, the frequency of reflected sound as heard by driver is
A rocket moves at a speed of directly towards a detector pole while emitting sound waves at frequency The frequency measured by the detector is (Assuming velocity of sound )
A source of sound moving towards a stationary observer with a certain velocity passes him with the same velocity. The ratio of the apparent frequencies when the source is moving towards the observer and when moving away from the observer is . Find the velocity of the source of sound.
In a car race, sound signals emitted by the two cars are detected by a detector on the straight track at the end of the race. The frequency observed for the two cars is and respectively, while the original frequency is for both the cars. The race ends with a separation of between the cars. Assume both cars move with constant velocity and velocity of sound is . Find the time taken by the winning car (in second).
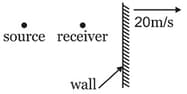
A source of sound having frequency and a receiver are located along the same line normal to the wall as shown in the figure. Both the source and the receiver are stationary and the wall recedes from the source with a velocity of . If the beat frequency registered by the receiver is , then what is the value of ? [velocity of sound = ]
In a car race, sound signals emitted by the two cars are detected by a detector on the straight track at the end of the race. The frequency observed for the two cars is and respectively, while the original frequency is for both the cars. The race ends with a separation of between the cars. Assume both cars move with constant velocity and velocity of sound is . Find the time taken by the winning car (in second).
A listener revolves along a circular path with constant speed of A stationary source of sound is situated outside away from the circular path. Speed of sound in air is If the ratio of maximum frequency to minimum frequency received by the listener is , what is the value of ?
A sound source and listener are both stationary and a strong wind is blowing. Is there a Doppler effect?
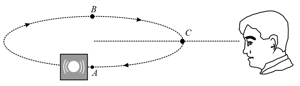
A small source of sound moves on a circle as shown in the figure and an observer is standing on Let and be the frequencies heard, when the source is at and respectively. Then,