Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Centripetal and Centrifugal Force and Centripetal Acceleration
Important Questions on Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
A car takes a round turn of radius with the velocity of . The centripetal force is:
A ball of mass attached to the end of a string of length is moving in a horizontal circle. The string will break if the tension is more than . What is the maximum speed with which the ball can be moved?
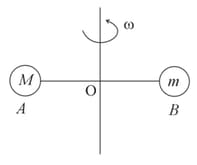
Two blocks of mass and connected to each other by a massless inextensible string of length are placed along a diameter of a turn table. The coefficient of friction between the table and is while there is no friction between and the table. The table is rotating with an angular velocity of rad about a vertical axis passing through its centre . The masses are placed along the diameter of the table on either side of the centre such that the mass is at a distance of from . The masses are observed to be at rest with respect to an observer on the turn table. Calculate the frictional force on .
Three particles, each of mass are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side length . The only forces acting on the particles are their mutual gravitational forces. It is desired that each particle moves in a circle while maintaining the original mutual separation . Find the initial velocity that should be given to each particle and also the time period of the circular motion.
A vehicle of mass is moving along a levelled curved road of radius with angular velocity of . The centripetal force acting on the vehicle is:
A small block of mass is tied to a spring of spring constant and length The other end of spring is fixed at a particular point If the block moves in a circular path on a smooth horizontal surface with constant angular velocity about point then tension in the spring is
A toy car of mass is maintained to move in a horizontal circle of radius with a velocity . If the centripetal force acting on it is , then the value of in is
Centripetal and centrifugal force cancel each other.
How is centripetal force related to centrifugal force?
Define centripetal force with its direction.
A body is revolving with a constant speed along a circle. If its direction of motion is reversed but the speed remains the same, then,
If a car moves on a circular banked road the centripetal force may be provided by :-
A stone of mass attached to a long string is whirled around in a horizontal circle at a speed of . The tension in the string is:
When a car of mass passes through a convex bridge of radius with velocity , then it exerts a force on it. What is the magnitude of the force?
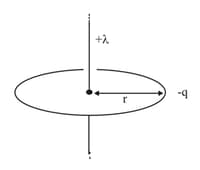
A particle of charge-q & mass moves in a circle of radius around an infinitely long line charge on linear charge density Then time period will be
Name the acceleration experienced by an object in a circular motion, along the radius, towards the centre of the circle.
A ring rotates about -axis as shown in figure. The plane of rotation is . At a certain instant the acceleration of a particle (shown in figure)
on the ring is Find magnitudes of angular acceleration of the ring and its angular velocity at that instant. Radius of the ring is :-
When a point on the rim of a radius wheel experiences a centripetal acceleration of what tangential acceleration does that point experience?
A body is projected with a speed at an angle ' ' with the honizontal. The radius of curvature of the trajectory when it makes an angle with the horizontal is (-acceleration due to gravity)
Two balls of masses and are attached by massless threads and . The length is . They are set in rotational motion in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis at with constant angular velocity . The ratio of lengths and for which the tension in threads are same will be,