A K Upadhyay and S Upadhyay Solutions for Chapter: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles, Exercise 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
A K Upadhyay Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - A K Upadhyay and S Upadhyay Solutions for Chapter: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles, Exercise 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles, Exercise 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MATHEMATICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from A K Upadhyay and S Upadhyay Solutions for Chapter: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles, Exercise 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
is a quadrilateral whose diagonal divides it into two parts, equal in area, then
In which of the following figures you find two polygons on the same base and between the same parallels?
In the below figure, area of parallelogram is
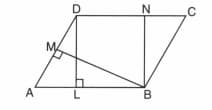
The mid-point of the sides of a triangle along with any of the vertices as the fourth point make a parallelogram of area equal to
Two parallelograms are on equal bases and between the same parallels. The ratio of their area is
are the mid points of sides of a parallelogram . If , then is
In a if are mid-points of respectively such that , then is
is a trapezium in which . If , then height of is
