Equilibrium of a Body
Important Questions on Equilibrium of a Body
The centre of gravity of a body which is in unstable equilibrium, lies
Explain how static equilibrium of a body is related to the potential energy? Give illustrations.
What do you mean by equilibrium state of a system? How many types of equilibrium are there?
What are the conditions of equilibrium of a body due to three forces?
What are the conditions of equilibrium of a body due to several coplanar forces?
A small sphere of radius is held against the inner surface of a larger sphere of radius The 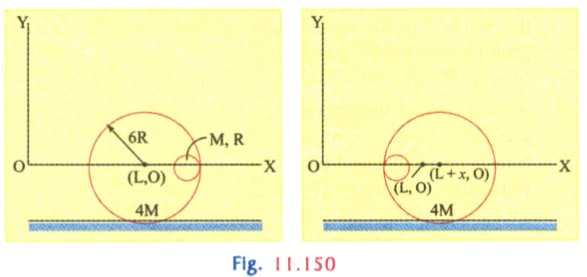
masses of large and small spheres are and respectively. The arrangement is placed on a horizontal table. There is no friction between any surfaces of contact. The small spheres is now released. Find the coordinates of the centre of the larger sphere when the smaller sphere reaches the other extreme position.
Two particles of masses and are situated on the and axes respectively at a distance and from the origin. Locate the centre of mass of the system.
Explain how the centre of gravity of a body distinguishes the stable, neutral and unstable equilibrium of a body.
What do you mean by the term ‘equilibrium of a body'? State and explain the conditions of equilibrium of a body acted upon by a number of co-planar forces.
A cube of uniform side and mass rests on a rough horizontal table. A horizontal force is applied normal to one of the faces at a point that is directly above the centre of the face at a height above the base. For what minimum value of , the cube begins to tip about an edge?
A door high and wide weighs . A hinge from the top and another from the bottom, each supports half the door's weight. Assume that the CG is at the geometrical centre of the door. Determine the horizontal and vertical force components exerted by each hinge on the door.
A solid cone of height has a circular base of radius . It rests on an inclined plane without slipping. What is the maximum angle of the inclined plane at which the cone is just on the point of toppling?
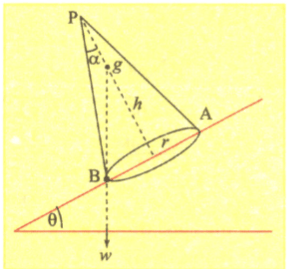
Give an example when and , yet the system is not in static equilibrium.
Three coplanar forces keep a body in equilibrium. Are they necessarily concurrent?
Draw a diagram indicating a body in equilibrium under the action of two forces.
A body is in equilibrium. Can it be in a state of uniform motion in a straight line?
Give an example of a body which is not in equilibrium even though the resultant of all the forces acting on it is zero.
A ping-pong ball is floating on the top of a vertical water jet. Is it in stable, unstable or in neutral equilibrium in the vertical direction?
If a body is not in translational equilibrium will the torque about any point be zero if the torque about some particular point is zero?
Explain the following carefully:
A ladder is at rest with its upper end against a wall and the lower end on the ground. Is it more likely to slip when a man stands on it at the bottom or at the top?

