Carnot Engine
Important Questions on Carnot Engine
A Carnot engine, whose efficiency is, takes in heat from a source maintained at a temperature of . It is desired to have an engine of efficiency . Then, the intake temperature for the same exhaust (sink) temperature must be
A carnot engine, whose efficiency is , takes in heat from a source maintained at a temperature of . It is desired to have an engine of efficiency . Then, the intake temperature for the same exhaust (sink) temperature must be
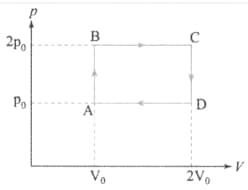
Helium gas goes through a cycle (consisting of two isochoric and two isobaric lines) as shown in Fig. . Efficiency of the cycle is nearly. (Assume the gas to be close to ideal gas)
A carnot engine takes of heat from a reservoir of and given it to a sink at . The Work done by the engine is
A carnot engine absorbs an amount of heat from reservoir at an absolute temperature and rejectes heat to a sink at a temperature of . The amount of heat rejected is
A Carnot engine whose low temperature reservoir is at has an efficiency of . It is desired to increase the efficiency to . By how many degree should the temperature of high temperature reservoir be increased ?
A Carnot reversible engine converts of heat input into work. When the temperature of the sink is reduced by , the efficiency of carnot cycle becomes . The temperature of the source and sink will be
Three designs are proposed for an engine operating between and . For of heat input, design A claims to produce of work, design claims to produce of work and design claims to produce of work. The design which is possible.
The efficiency of a Carnot's heat engine is , when the temperature of the source is and that of sink is . The efficiency of another carnot engine is also The temperatures of source and sink of the second engine are respectively
A carnot engine operating between temperatures and has efficiency . When is lowered by , its efficiency increases to . Then and are, respectively
An ideal refrigerator has a freezer at a temperature of . The coefficient of performance of the engine is . The temperature of the air (to which heat is rejected) is :
An ideal carnot engine takes heat from a source at does some work and delivers the remaining energy to a heat sink at . If of heat is taken from the source, how much work is done ? How much heat is delivered to the sink ?
Compare the actual efficiency with the theoretical maximum efficiency. A carnot-type engine is designed to operate between and . Assuming that the engine actually produces of mechanical energy per kilocalorie of heat absorbed.
A carnot engine operates between and . What is its efficiency ?
What is a carnot refrigerator ? Find the relation between the coefficient of performance of a carnot refrigerator and the efficiency of a carnot heat engine.
What is second law of thermodynamics, does it provide which first law cannot?
What is carnot theorem ?
Draw the diagram and diagram of a carnot cycle and explain these. What is the efficiency of a carnot engine.
Oceans contain enormous thermal energies. Can this energy be utilised to run a heat engine ?
What is the usefulness of a Carnot engine if it cannot be realised in practice?

