Elastic and Inelastic Collisions in One Dimension
Important Questions on Elastic and Inelastic Collisions in One Dimension
A bullet of mass is fired with a velocity at an angle with the horizontal. At the highest point of its trajectory, it collides head-on with a bob of mass suspended by a massless string of length and gets embedded in the bob. After the collision, the string moves through an angle of . Find the angle . .
Consider that light consists of very light elastic corpuscles. Show that laws of reflection of light follows from the conservation laws of momentum and kinetic energy.
When is a collision called an inelastic collision? When is it called a perfectly inelastic collision? Find the loss in kinetic energy of two bodies of equal mass having an inelastic collision. When this loss of energy has the maximum value?
Explain what happens when a very heavy body has a head-on elastic collision with a very light body at rest.
Explain what happens when a very light has a head-on elastic collision with a very heavy body at rest.
Explain what happens when a body has a head-on elastic collision with another body of equal mass.
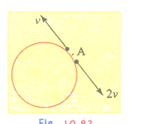
Two small particles of equal masses start moving in opposite directions from a point in a horizontal circular orbit. Their tangential velocities are respectively, as shown in the figure. Between collision, the particles move at constant speeds. After making how many elastic collisions, other than that at these two particles will again reach the point ?
In an inelastic collision the final kinetic energy is always less than the kinetic energy of the system.
State if each of the following statements is true or false:
In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the momentum and energy of each body is conserved.
In an inelastic collision of two bodies which of the quantities would remain unchanged total kinetic energy, total momentum and total energy?
A point mass of collides elastically with a stationary point mass of . After their collision, the mass reverses its direction and moves with a speed of . Which of the following statements is correct for a system of these two masses?
Define elastic collision. Show that in an elastic collision, the relative velocity of approach before collision is equal to the relative velocity of separation after collision?

