Position-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs
Important Questions on Position-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs
A train moves from one station to another in two hours. Its speed during the motion is shown in the graph, Fig.
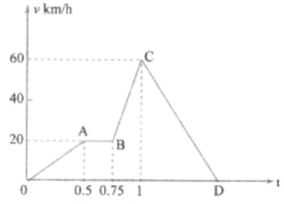
distance covered during the time interval from to hour.
A train moves from one station to another in two hours. Its speed during the motion is shown in the graph, Fig.
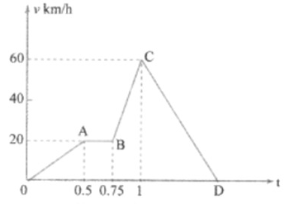
Calculate maximum acceleration during the journey
The velocity-time curve is shown in Fig.The corresponding acceleration time curve will be
A body is at rest at . At , it starts moving in the positive -direction with a constant acceleration. At the same instant, another body passes through moving in the positive -direction with a constant speed. The position of the first body is given by after time and that of the second body by after the same time interval. Which of the following graphs in Fig.correctly describes as a function of time?
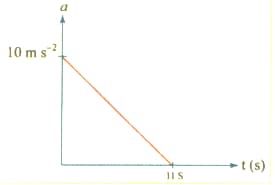
A particle starts from rest. Its acceleration versus time graph is shown in the Figure . The maximum speed attained by the particle is
The velocity-displacement graph of a particle moving along a straight line is shown in Fig. Which one of the following acceleration-distance graphs corresponds to the velocity-distance graph?
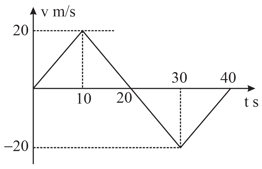
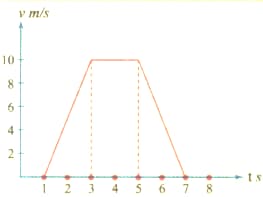
For the velocity-time graph shown in Fig. The distance covered by the body in the last two seconds of its motion is what fraction of the total distance covered in all the seven seconds?
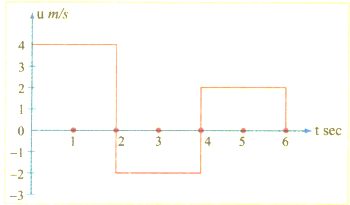
The velocity-time graph of a body moving in a straight line is shown in Fig. The displacement and distance travelled by the body in seconds are respectively
The velocity-time curve for a body projected vertically upward is
A particle is thrown vertically upwards. The graph between its speed and time is given by (neglecting for resistance) the figure [See Fig. ].
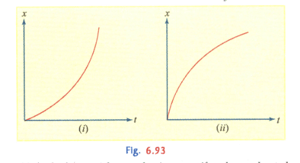
Fig. (i) and show the displacement-time graph of two particles moving along -axis. We can say that:
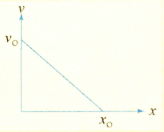
The displacement-time graph of two particles and are straight lines inclined at angles and with time axis. The ratio of is:
Explain how can we get displacement of a particle in a certain time-interval from its velocity-time graph.
Prove that instantaneous acceleration is the slope of the velocity-time curve at the relevant point.
Define instantaneous velocity. Explain how we may get instantaneous velocity of a particle moving with a variable velocity if we know its displacement time graph.
Show that the instantaneous acceleration at any point in the velocity-time graph equals the slope of the tangent to the graph at that point. Which one is more important in the laws of mechanics - the average acceleration or the instantaneous acceleration ?
A train is moving along a straight track. Explain what would be the nature of its velocity-time graph in the following case: If its acceleration is increasing.
A train is moving along a straight track. Explain what would be the nature of its velocity-time graph in the following case: If it is moving with a uniform acceleration.
The area under acceleration–time graph represents

