Academic Experts Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: Motion of a Charged Particle in Electric and Magnetic Field
Academic Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Academic Experts Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: Motion of a Charged Particle in Electric and Magnetic Field
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 1: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: Motion of a Charged Particle in Electric and Magnetic Field with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for MHT-CET Physics (Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Academic Experts Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: Motion of a Charged Particle in Electric and Magnetic Field with Hints & Solutions
An electron (mass, charge ) experiences no deflection if subjected to an electric field of and a magnetic field of . Both the fields are normal to the path of electron and to each other. If the electric field is removed, then the electron will revolve in an orbit of radius
An electron moving with a velocity at a point in a magnetic field experiences a force If the electron is moving with a velocity at the same point, it experiences a force . The force electron would experience if it were moving with a velocity at the same point is
A particle of charge and mass starts moving from the origin in presence of an electric field and a magnetic field with a velocity . The speed of the particle will become after a time . Determine .
A particle moving with a velocity having specific charge enters in a region of magnetic field having width at an angle to the boundary of magnetic field. Find the angle of emergence .
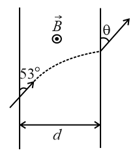
A particle of mass and charge , moves with a constant velocity , along the positive -direction. It enters a region containing a uniform magnetic field , directed along the negative -direction, extending from to The minimum value of required, so that the particle can just enter the region , is
A particle of mass and charge enters in an uniform magnetic field of as shown in the figure. The speed of the particle is . The distance will be
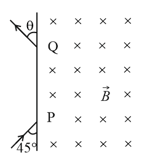
Two particles and of masses and respectively, having the same charge are moving in a plane. A uniform magnetic field exists perpendicular to this plane. The speeds of the particles are and respectively and the trajectories are as shown in the figure. Then
A particle of charge and mass , moving under the influence of a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field , follows trajectory from to , as shown in the figure. The velocities at and are and , respectively. Which of the following options are correct?
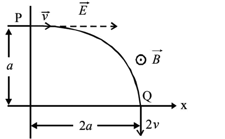
(a)
(b)
(c) Rate of work done by magnetic field at any point is zero.
(d) Rate of work done by electric field at any point is zero.