Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Achieve CUET (UG) Physics Practice Book solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
An observer whose least distance of distinct vision is , views his own face in a convex mirror of radius of curvature . The magnification produced can not exceed?
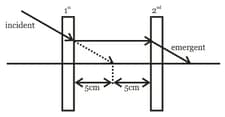
Look at the ray diagram shown, what will be the focal length of the 1st and the 2nd lens, if the incident light ray passes without any deviation?
The centre of the lens is called:
Why do we use paraxial rays?
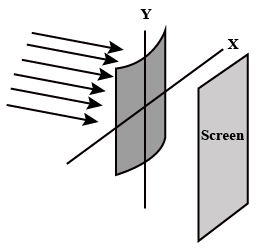
Consider a plane parallel beam of light incident on a plano-cylindrical lens as shown. Which of the following will you observe on a screen placed at the focal plane of the lens?
Which eyepiece called negative eyepiece?
Linear magnification is
A telescope that uses two converging lenses is called
