Aidan Gill, Heidi Foxford and, Dorothy Warren Solutions for Chapter: Light, Exercise 3: Exercise 3
Aidan Gill Science Solutions for Exercise - Aidan Gill, Heidi Foxford and, Dorothy Warren Solutions for Chapter: Light, Exercise 3: Exercise 3
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 7: Light, Exercise 3: Exercise 3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Stage 8 : Workbook solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Aidan Gill, Heidi Foxford and, Dorothy Warren Solutions for Chapter: Light, Exercise 3: Exercise 3 with Hints & Solutions
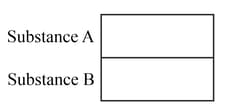
The diagram shows arrangements of two different substances, A and B, that are placed next to each other so they touch. The table shows the possible combinations of A and B. Choose which combinations will show refraction at the boundary between A and B. Choose the pairs given below which shows refraction.
The diagram shows the surface of a lake of water. A lamp has been placed on the bottom of the lake.
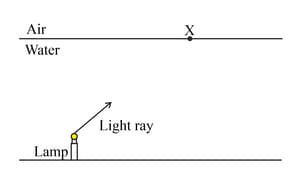
Add a normal line at point 'X'.
The diagram shows the surface of a lake of water. A lamp has been placed on the bottom of the lake.
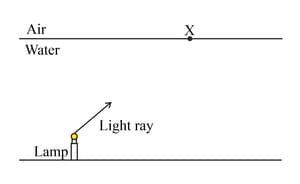
Describe how the direction light ray changes as it enters the air.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
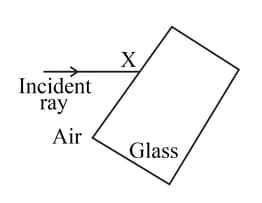
Think about what happens at point X. Draw a normal at X and the path of the refracted ray inside the glass block.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
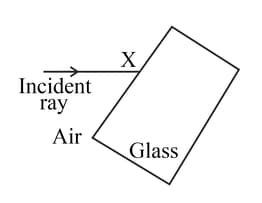
Add the label 'Y' where your first refracted glass ray leaves the glass block.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
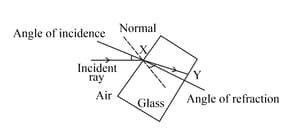
Think about what happens at the point you have labelled Y. Draw a normal at Y and the path of the refracted ray through the air to the right of the glass block.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
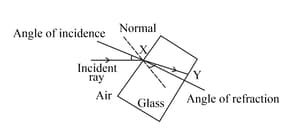
Add the label 'Z ' to the angle of refraction between the normal at Y and the refracted ray.
Look at the diagram of a glass block surrounded by air. The incident ray is shown.
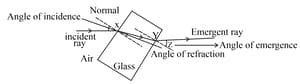
State the connection between the original angle of incidence at point X and the final angle of refraction Z at point Y.
