Raoult's Law
Important Questions on Raoult's Law
Two liquids and are miscible over the whole range of composition and may be treated as ideal (obeying Raoult's law.) At the vapour pressure of pure is and of pure is mixture of A and is distilled at this temperature. A small amount of the distillate is collected and and redistilled at what is the mole percent of in the second distillate ?
The vapor pressure of chlorobenzene and water at different temperatures are
At what temperature will steam-distillation under a total pressure of ?
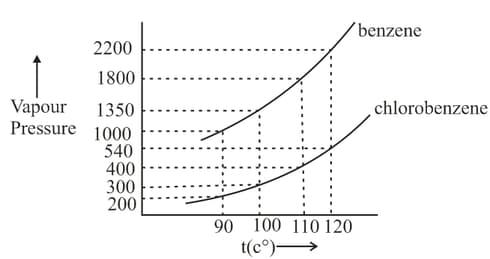
Assuming the formation of an ideal solution, determine the boiling point of a mixture containing benzene (molar mass ) and chlorobenzene (molar mass ) using the following against an external pressure of Torr.
Consider two liquids having pure vapour pressures forming an ideal solution. The plot of (where and are the mole fraction of liquid in liquid and vapour phase respectively) is linear with slope and intercepts respectively:
A solution is prepared by mixing of and of If vapour pressure of and at are and respectively, the mole fraction of in vapour form is:
The relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the mole fraction of the solute. This is the statement of:
For a dilute solution containing of a non- electrolyte solute. in of water, the elevation in boiling point at atm pressure pressure is Assuming concentration of solute is much lower than the concentration of solvent, the vapour pressure of ) of the solution is (take
At , the vapour pressure in millimeters of mercury of a methanol-ethanol solution is represented by the equation, , where is the mole fraction of methanol. Then the value of is:
If and are the vapour pressures of a solvent and its solution, respectively, and and are the mole fractions of the solvent and non-volatile solute, respectively, then the correct relation is:
The vapour pressure of pure water at. If of glucose is added toof water at , the vapour pressure of resulting solution will be
A very small amount of a non-volatile solute (non-associative, non-dissociative) is dissolved in of a solvent. At room temperature, vapour pressure of this solution is of while that of pure solvent is of . If the freezing temperature of this solution is lower than that of pure solvent, what is the value of cryoscopic constant of solvent (in ) ? Round off your answer to the nearest whole number. Report your answer as (zero) if you find data insufficient. Given: Molar mass of solvent .
Following is false when in a volatile solvent and a non volatile solute is mixed (where symbols have their usual meaning):
The vapour pressure of two pure isomeric liquids and are and , respectively, at a given temperature. Assuming a solution of these components to obey Raoult’s law. The mole fraction of component in the vapour phase in equilibrium with the solution containing equal amounts of and , at the same temperature, is
Mole fraction of the toluene in the vapor phase which is in equilibrium with a solution of benzene and toluene having of each is:
The vapor pressure of a pure liquid is . The vapor pressure of this liquid in a solution with liquid is . Mole fraction of in the solution, if it obeys Raoult’s law is:
A solution at is composed of of benzene and of toluene. If the vapour pressure of pure benzene and pure toluene at this temperature are torr and torr, respectively, then the total vapour pressure of the solution and the benzene mole fraction in equilibrium with it will be, respectively:
On mixing heptane and octane form an ideal solution at , the vapour pressures of the two liquid components (heptane and octane) are and , respectively. The vapour pressure of the solution obtained by mixing of heptane and of octane will be (molar mass of heptane and of octane)
Two liquids and form an ideal solution. At , the vapour pressure of the solution containing of and of is . At the same temperature, if of is further added to the solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by . Vapour pressure (in ) of and in their pure states will be, respectively
At , the vapour pressure of a pure liquid is and that of a pure liquid is . If a mixture solution of and boils at , at pressure, the amount of in the mixture is
A mixture of ethyl alcohol and propyl alcohol has a vapour pressure of at . The vapour pressure of propyl alcohol is . If the mole fraction of ethyl alcohol is , its vapour pressure (in ) at the same temperature will be

