Energy Stored in a Capacitor
Important Questions on Energy Stored in a Capacitor
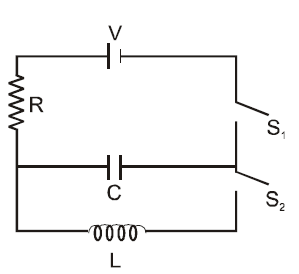
In an circuit as shown below both switches are open initially. Now the switch is closed, kept open. ( is the charge on the capacitor and is capacitive time constant). Which of the following statement is correct?
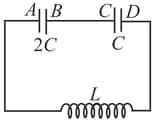
Two capacitors of capacitances are connected in series with an inductor of inductance L. Initially capacitors have charges such that Initial current in the circuit is zero. Find The maximum current that will flow in the circuit and the potential difference across each capacitor at that instant.
Two parallel plate capacitors and have the same separation between the plates. The plate areas of and are and , respectively. A slab of dielectric constant (relative permittivity ) has dimensions such that it can exactly fill the space between the plates of the capacitor .
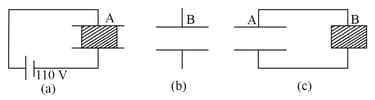
The dielectric slab is placed inside as shown in the figure . is charged to a potential difference of . Calculate the capacitance of and energy stored in it.
The battery is disconnected and then the dielectric also slab is moved from . Find the work done by the external agency in removing the slab from .
The same dielectric slab is now placed inside , filling it completely. The two capacitors and are then connected as shown in the figure . Calculate the energy stored in the system.
The figure shows two identical parallel plate capacitors connected to a battery with the switch closed. The switch is now opened and the free space between the plates of the capacitors is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant (or relative permittivity) . Find the ratio of the total electrostatic energy stored in both capacitors before and after the introduction of the dielectric.
The circular plates and of a parallel plate air capacitor have a diameter of and are apart. The plates and of a similar capacitor have a diameter of and are apart. The plate is earthed. Plates and are connected together. Plate is connected to the positive pole of a battery whose negative is earthed. Calculate
The combined capacitance of the arrangement and
The energy stored in it.
A parallel plate condenser with a dielectric of a dielectric constant between the plates has a capacity and is charged to a potential . The dielectric slab is slowly removed from between the plates and then reinserted. The net-work done by the system in this process is
A battery is used to charge a parallel plate capacitor till the potential difference between the plates becomes equal to the electromotive force of the battery. The ratio of the energy stored in the capacitor and the work done by the battery will be
A capacitor is charged as shown in the figure. The percentage of its stored energy dissipated after the switch is turned to the position is
An isolated metallic object is charged in vacuum to a potential using a suitable source, its electrostatic energy being . It is then disconnected from the source and immersed in a large volume of dielectric with dielectric constant . The electrostatic energy of the sphere in the dielectric is:
A parallel plate condenser with plate separation is charged with the help of a battery, so that energy is stored in the system. A plate of dielectric constant and thickness is placed between the plates of the condenser, the battery is disconnected before placing the plate, then new energy will be
A parallel plate condenser with plate separation is charged with the help of a battery so that energy is stored in the system. A plate of dielectric constant and thickness is placed between the plates of condenser while battery remains connected. The new energy of the system will be,
A parallel plate condenser of capacity is connected to a battery and is charged to potential . Another condenser of capacity is connected to another battery and is charged to potential The charging batteries are removed and now the condensers are connected in such a way that the positive plate of
one is connected to negative plate of another. The final energy of this system is
The plate separation in a parallel plate condenser is and plate area is . If it is charged to volt & battery is disconnected then the work done in increasing the plate separation to will be
The work done against electric forces in increasing the potential difference of a condenser from to is . The work done in increasing its potential difference from to will be (consider capacitance of capacitor remain constant)
A parallel-plate capacitor of plate area and plate separation is charged by a ideal battery of and then the battery is disconnected. A slab of dielectric constant is then inserted between the plates of the capacitor so as to fill the whole space between the plates. Find the change in potential energy of the system in the process of inserting the slab.
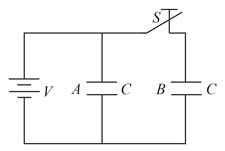
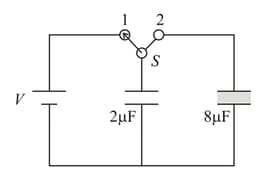
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The switch is open for a long time and then closed and again steady state reached then
Find the charge flown through the battery after the switch is closed.
Find the work done by the battery after the switch is closed.
Find the change in energy stored in the system of capacitors.
Find the heat developed in the system after the switch is closed.
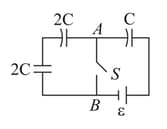
Find out the charges on the three capacitors connected to a battery as shown in figure. Take 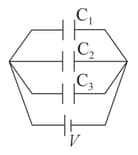
Find out the work done by the battery during the process of charging (initially all the capacitors are uncharged)
Find out the total energy stored in the capacitors.
A conducting sphere of radius is attached to an insulating handle. Another conducting sphere of radius R is mounted on an insulating stand. is initially uncharged. is given a charge , brought into contact with and removed. is then recharged such that the charge on it is again & it is again brought into contact with & removed. This procedure is repeated times
(a) Find the electrostatic energy of after n such contacts with .
(b) What is the limiting value of this energy as ?
A uniformly charged sphere of the radius has the potential of at the surface. The energy density near the surface of the sphere will be

