Acceleration Due to Gravity
Important Questions on Acceleration Due to Gravity
The value of mass and radius of sun are given by and , respectively. The pressure at the centre is about
A solid sphere of mass and radius is placed inside a hollow spherical shell of mass and radius find gravitational field intensity at:
here coordinate is measured from the point of contact of the sphere and the shell.
The variation of acceleration due to gravity with distance d from centre of the earth is best represented by ( Earth's radius)
The height at which the acceleration due to gravity becomes (where the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth) in terms of , the radius of the earth is,
If and are the accelerations due to gravity on the surfaces of the earth and the moon respectively and if Millikan's oil drop experiment could be performed on the two surfaces, one will find the ratio to be
A planet of radius (radius of Earth) has the same mass density as Earth. Scientists dig a well of depth on it and lower a wire of the same length and of linear mass density into it. If the wire is not touching anywhere, the force applied at the top of the wire by a person holding it in place is (take the radius of Earth and the acceleration due to gravity on Earth is )
An object is weighed at the equator by a beam balance and a spring balance, giving readings and , respectively. It is again weighed in the same manner at the north pole giving readings of and , respectively. Assume that intensity of earth gravitational field is the same every where on the earth’s surface and that the balances are quite sensitive.
The gravitational field in a region is given by Find out the work done (in joule) in displacing a particle of mass by along the line
Assuming that the moon is a sphere of the same mean density as that of the earth and one quarter of its radius, the length of a seconds pendulum on the moon (its length on the earth’s surface is ) is
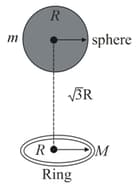
A uniform ring of mass is lying at a distance from the centre of a uniform sphere of mass just below the sphere as shown in the figure where is the radius of the ring as well as that of the sphere. Then gravitational force exerted by the ring on the sphere is
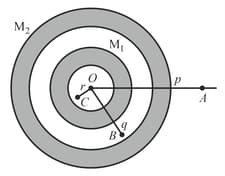
Two concentric shells of uniform density of mass and are situated as shown in the figure. The forces experienced by a particle of mass when placed at positions and respectively are (given and ).
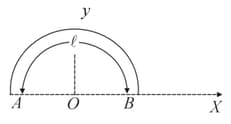
Gravitational field at the centre of a semicircle formed by a thin wire of mass and length as shown in the figure is
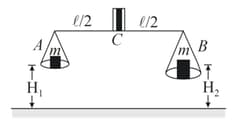
Two blocks of masses each are hung from a balance as shown in the figure. The scale pan is at height whereas scale pan is at height . Net torque of weights acting on the system about point , will be (length of the rod is and
The acceleration due to gravity at a height the radius of the earth above earth’s surface is . Find out its approximate value at a point at an equal distance below the surface of the earth.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator. (a) By what percentage is the balance reading less than his true weight? (b) If the speed of earth’s rotation is increased by such an amount that the balance reading is half the true weight, what will be the length of the day in this case?

