Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 13: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
A liquid is kept in a cylindrical vessel which is rotated about its axis. The liquid rises at the sides. If the radius of the vessel is and the speed of rotation is , The difference in the height of the liquid at the centre of the vessel and its sides will be
Pressure gradient in a static fluid is represented by -direction is vertically upwards, and -axis is along horizontal, is density of fluid):
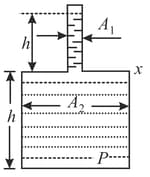
The vessel shown in the figure has two sections of the area of cross-section and . A liquid of density fills both the sections, up to height in each. Neglecting atmospheric pressure.
A cubical block of wood of edge and mass floats on a tank of water with oil of relative density Thickness of oil is above water. When the block attains equilibrium with four of its sides edges vertical:
Following are some statements about buoyant force, select incorrect statement/statements. (Liquid is of uniform density)
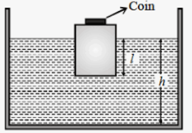
A wooden block with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as shown in figure. The distance and are shown here. After some time the coin falls into the water. Then :
A block of densityand mass is suspended by a spring stiffness The other end of the spring is attached to a fixed support. The block is completely submerged in a liquid of density If the block is in equilibrium position then,
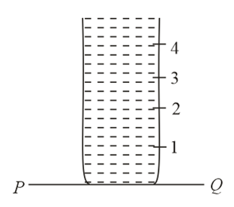
A cylindrical vessel ofheight is kept filled up to the brim as shown in the figure. It has four holes which are respectively at heights of and from the horizontal floor The water falling at the maximum horizontal distance from the vessel comes from