Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Wave Optics, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Wave Optics, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 31: Wave Optics, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Wave Optics, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1 with Hints & Solutions
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities and are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are,
A two-slit Young's interference experiment is done with monochromatic light of wavelength . The slits are apart. The fringes are observed on a screen placed away from the slits. Now a transparent plate of thickness is placed in front of one of the slits and it is found that the interference pattern shifts by . The refractive index of the transparent plate is , find ?
When an unpolarized light of intensity is incident on a polarizing sheet, the intensity of the light which does not get transmitted is:
A single-slit diffraction pattern is obtained using a beam of red light. What happens if red light is replaced by blue light?
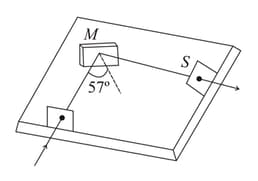
The figure shows a glass plate placed vertically on a horizontal table with a beam of unpolarised light falling on its surface at with the normal. The electric vectors in the reflected light on the screen will vibrate with respect to the plane of incidence,
Two point white dots are apart on a black paper. They are viewed by an eye having a pupil with diameter . Approximately, what is the maximum distance at which these dots can be resolved by the eye? [Take wavelength of .]
The resolving power of a telescope is more when its objective lens has
Interference is observed due to two coherent sources and separated by a distance along the -axis where is the wavelength of the source. A detector is moved on the positive -axis. The number of points on the -axis excluding the points, and at which maximum will be observed is