Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 5: Exercise-5
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 5: Exercise-5
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Solutions, Exercise 5: Exercise-5 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 5: Exercise-5 with Hints & Solutions
Dry air was passed through bulbs containing a solution of grams of non-volatile electrolytic solute in grams of water, then through bulbs containing pure water at the same temperature and finally through a tube in which pumice moistened with strong was kept. The water bulbs lost grams and the sulphuric acid tube gained grams. Calculate the molecular weight of solute.
Calculate the freezing point of a solution of a non-volatile solute in an unknown solvent of molar mass having mole fraction of solvent equal to . Given that latent heat of fusion of solid solvent freezing point of solvent and
At a constant temperature, will be the maximum for which of the following processes:
The freezing point of aqueous solution that contains urea, and of glucose is (given of water and asume molarity = molality).
Osmotic pressure of solution of glucose is and that of solution of cane sugar is . The osmotic pressure of the mixture containing equal volumes of the two solutions will be:
Consider two liquids having pure vapour pressures forming an ideal solution. The plot of (where and are the mole fraction of liquid in liquid and vapour phase respectively) is linear with slope and intercepts respectively:
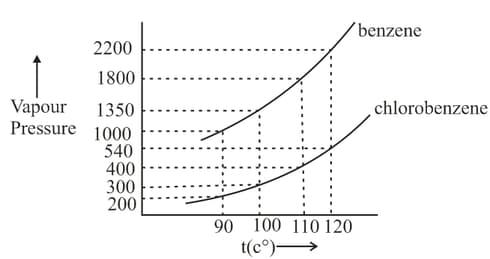
Assuming the formation of an ideal solution, determine the boiling point of a mixture containing benzene (molar mass ) and chlorobenzene (molar mass ) using the following against an external pressure of Torr.
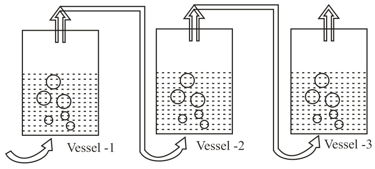
Dry air is slowly passed through three solutions of different concentrations, and ; each containing (non volatile) as solute and water as solvent, as shown in the Fig. If the vessel gains weight and the vessel loses weight, then