Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Mechanics of Solids and Fluids, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Mechanics of Solids and Fluids, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Mechanics of Solids and Fluids, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course BITSAT solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Mechanics of Solids and Fluids, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
In Poiseuilli's method of determination of coefficient of viscosity, the physical quantity that requires greater accuracy in measurement is
According to Newton, viscous force is given by
where coefficient of viscosity, so dimensions of will be :
The work done in blowing a soap bubble of radius is surface tension of the soap solution is
The radii of two soap bubbles are and . In isothermal conditions, two meet together in a vacuum. Then the radius of the resultant bubble is given by:
If work done to make a bubble of volume with soap solution is , then using same solution work done to make a bubble of volume is :
The force required to drag a circular ring flat plate of radius on the surface of water is (ST of water is dyne/cm):
The work done in increasing the size of a rectangular soap film with dimensions to is The surface tension of film is :
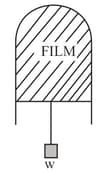
A thin liquid film formed between a U-shaped wire and a light slider supports a weight of (see figure). The length of the slider is and its weight negligible. The surface tension of the liquid film is :