Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Exercise-1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Exercise-1 with Hints & Solutions
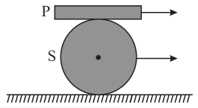
A plank is placed on a solid cylinder , which rolls on a horizontal surface. The two are of equal mass. There is no slipping at any of the surfaces in contact. The ratio of the kinetic energy of to the kinetic energy of is
The velocity of centre of mass of a disc rolling on an inclined plane changes from to at any instant of time. If is the mass of disc then increases in its kinetic energy will be
A uniform thin ring of mass rolls without slipping on a horizontal surface with a linear velocity of . The kinetic energy of the ring is :
The velocity of simple pendulum is maximum at
Two springs with spring constants and are stretched by the same force. The ratio of potential energy stored in spring will be:
The law of conservation of energy implies that the
A rubber ball is dropped from a height of on a plane. On bouncing, it rises to The ball loses its velocity on bouncing by a factor of,
Two balls having mass and are approaching each other with velocities and respectively on the horizontal frictionless surface. They undergo a head-on elastic collision. Find out the maximum potential energy of deformation.
