Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: What's Inside the Nucleus?, Exercise 13: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY
Annie Termaat Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: What's Inside the Nucleus?, Exercise 13: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 7: What's Inside the Nucleus?, Exercise 13: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MYP By Concept 4&5 Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Annie Termaat and Christopher Talbot Solutions for Chapter: What's Inside the Nucleus?, Exercise 13: SOME SUMMATIVE PROBLEMS TO TRY with Hints & Solutions
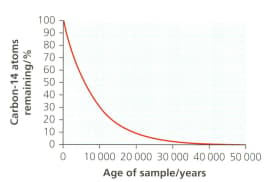
Estimate the half-life of carbon-14 with reference to the diagram.
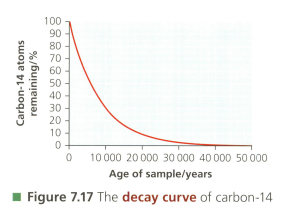
Evaluate the suitability of this isotope to date artefacts linked to the arrival of Australian Aboriginal peoples, who definitely reached the continent more than years ago.
Describe using a nuclear equation beta decay of iron- to cobalt-, a positron and gamma radiation.
Bromine consists of two isotopes and . Data booklets usually give the approximate value for the relative atomic mass of bromine as . Is the accurate value just above or just below ?
Copper consists of two isotopes, . The relative atomic mass of copper is . Which of these isotopes is present in the greater abundance?
A Geiger-Muller tube is used to measure the radiation at different distances from a source emitting alpha and gamma radiation. As the Geiger-Muller tube was gradually moved away from the source, it was found that the level of radiation fell very rapidly over the first few centimetres. However after that the radiation fell more slowly. Explain these observations.
In 1930, the physicist Paul Dirac proposed that all the fundamental particles have antiparticles whose electrical properties are opposite to the familiar particles.
Predict the charge on the antielectron and write its nuclide symbol.
In 1932, the American physicist Carl Anderson (1905-1991) discovered the 'anti-electron' (now called a positron) by allowing cosmic rays to pass through a cloud chamber when particles and anti-particles collide they annihilate each other and are converted into energy.
Calculate using Einstein's equation , the energy produced by an 'electron-positron annihilation'. Assume the mass of electron to be and the speed of light (c) to be . Your answer should be in joules.
