Assam Board Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
Assam Board Physics Solutions for Exercise - Assam Board Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS PART-1 TEXTBOOK FOR CLASS XII solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Assam Board Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 2: ADDITIONAL EXERCISES with Hints & Solutions
A uniform magnetic field of exists in a cylindrical region of radius , its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying current of in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of ?
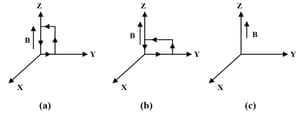
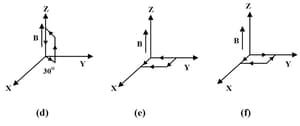
A uniform magnetic field of is established along the positive z-direction. A rectangular loop of sides and carries a current of . What is the torque on the loop in the different cases shown in the figure? What is the force on each case? Which case corresponds to a stable equilibrium?
A circular coil of turns and radius is placed in a uniform magnetic field of normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is , what is the total torque on the coil?
A circular coil of turns and radius is placed in a uniform magnetic field of normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is , what is the total force on the coil,
A circular coil of turns and radius is placed in a uniform magnetic field of normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is , what is the average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area and the free electron density in copper is given to be about .)
A solenoid long and of radius has layers of windings of turns each. A long wire of mass lies inside the solenoid (near its centre) normal to its axis; both the wire and the axis of the solenoid are in the horizontal plane. The wire is connected through two leads parallel to the axis of the solenoid to an external battery which supplies a current of in the wire. What value of current (with an appropriate sense of circulation) in the windings of the solenoid can support the weight of the wire?
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of and the metre shows full-scale deflection for a current of . How will you convert the metre into a voltmeter of range to?
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of , and the metre shows full-scale deflection for a current of . How will you convert the metre into an ammeter of range to ?