B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: DPP
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: DPP
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: DPP with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Electrostatics and Current Electricity JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Flux and Gauss's Law, Exercise 2: DPP with Hints & Solutions
A Gaussian surface encloses two charges and . The field at is,
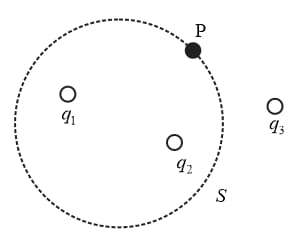
where , and are the field contributed by , and at respectively.
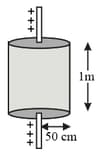
A charge is placed at the centre of the open end of cylindrical vessel. The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is,
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius . The charge per length of the wire is coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius and length symmetrically encloses the wire as shown in the figure. The total electric flux passing through the cylindrical surface is,
In a region of space having a spherically symmetric distribution of charge, the electric flux enclosed by a concentric spherical Gaussian surface varies with a radius as
where and are the constants.
The electric field strength in the region is given as,
In a region of space, the electric field is in the -direction and proportional to , i.e., . Consider an imaginary cubical volume of edge with its edges parallel to the axes of coordinates. The charge inside this volume will be,
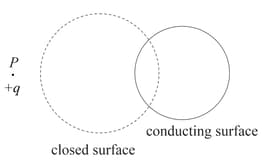
The figure shows a closed surface that intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at the point , the flux of the electric field through the closed surface,
The figure shows a neutral metallic sphere with a point charge placed near its surface. Electrostatic equilibrium conditions exist on metallic sphere. Mark the correct statements.
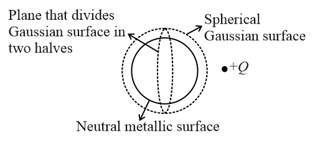
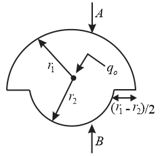
and are semi-spherical surfaces of radius and with and as the electric fields at their surfaces. Charge is placed as shown. What is the condition which may be satisfied?