DPP
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - DPP
Simple step-by-step solutions to DPP questions of Electric Flux and Gauss's Law from Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Electrostatics and Current Electricity JEE Main & Advanced. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from DPP with Hints & Solutions
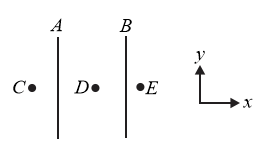
An infinitely long wire is kept along -axis from to , having uniform linear charge density . The electric field at the point will be,
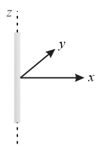
Two concentric conducting thin spherical shells and having radii and are charged to and . The electrical field along a line (passing through the centre) is,
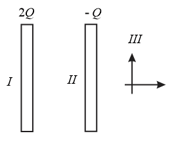
Two large conducting thin plates are placed parallel to each other. They carry the charges as shown. The variation of magnitude of electric field in space due to this system is best given by,
A positively charged sphere of radius carries a volume charge density (see figure). A spherical cavity of radius is then scooped out and left empty, as shown. is the centre of the sphere and is the centre of the cavity. What is the direction and magnitude of the electric field at point ?
A charge is placed at some distance along the axis of a uniformly charged disc of surface charge density . The flux due to the charge through the disc is . The electric force on charge exerted by the disc is,
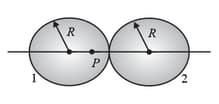
The figure shows, in cross-section, two solid spheres with uniformly distributed charge throughout their volumes. Each has a radius . The point lies on a line connecting the centres of the spheres, at a radial distance from the centre of the sphere . If the net electric field at a point is zero, what is the ratio of the total charges?
A very long uniformly charged circular cylinder (radius ) has a surface charge density . A very long uniformly charged line charge (linear charge density ) is placed along the cylinder axis. If the electric field intensity vector outside the cylinder is zero, then:
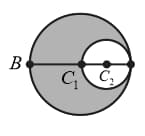
Two infinite plane sheets and are shown in the figure. The surface charge densities on and are and respectively. , and are three points where electric fields (in ) are , and respectively.