B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current, Exercise 3: DPP
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current, Exercise 3: DPP
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: Alternating Current, Exercise 3: DPP with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Alternating Current, Exercise 3: DPP with Hints & Solutions
The self-inductance of a choke coil is . When it is connected with a DC source, then the loss of power is . When it is connected with AC source, loss of power is . The frequency of AC source will be
A group of electric lamps having a total power rating of is supplied by an ac voltage . The r.m.s. value of the circuit current is
In an circuit, the inductive reactance is equal to the resistance of the circuit. An emf is applied to the circuit. The power consumed in the circuit is
An series circuit with a resistance of is connected to an ac source of (r.m.s.) and angular frequency . When only the capacitor is removed, the current lags behind the voltage by . When only the inductor is removed, the current leads the voltage by . The average power dissipated is
In the circuit shown in figure, neglecting source resistance, the voltmeter and ammeter readings, respectively, will be
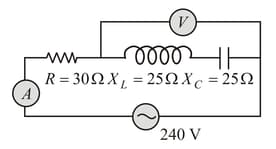
In the circuit shown in the figure, the ac source gives a voltage . Neglecting source resistance, the voltmeter and ammeter readings will be
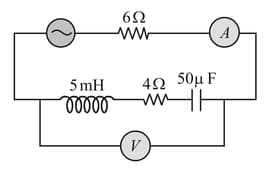
An ac source of angular frequency is fed across a resistor and a capacitor in series. The current registered is . If now, the frequency of the source is changed to (but maintaining the same voltage), the current in the circuit is found to be halved. Calculate the ratio of reactance to resistance at the original frequency .
The diagram shows a capacitor and a resistor connected in series to an ac source. and are voltmeters and is an ammeter.
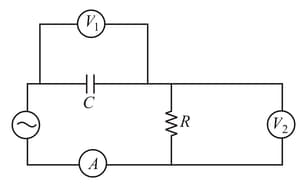
Consider the following statements:
. Readings in and are always in phase.
. Reading in is ahead in phase with reading in .
. Readings in and are always in phase.
Which of these statements are/is correct?
