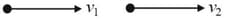B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Center of Mass, Exercise 4: DPP 1.4
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Center of Mass, Exercise 4: DPP 1.4
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 1: Center of Mass, Exercise 4: DPP 1.4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Mechanics - II JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Center of Mass, Exercise 4: DPP 1.4 with Hints & Solutions
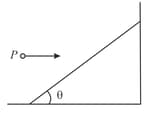
In the figure shown, a particle strikes the inclined smooth plane horizontally and rebounds vertically. If the angle is then, the coefficient of restitution is,
The smooth objects, with a coefficient of restitution , collides directly and bounces as shown:
Just before impact
Just after impact
Newton's law of restitution gives,
A particle of mass , moving with an initial speed , collides with another particle of the same mass kept at rest. If after collision, total energy becomes , then,
A ball of mass approaches a wall of mass with speed along the normal to the wall. The speed of wall is towards the ball. The speed of the ball after an elastic collision with the wall will be,
A ball strikes a horizontal floor at an angle, . The coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor is, . The fraction of its kinetic energy lost in the collision is,
In one-dimensional collision of two particles, the velocities interchanged when,
(i) collision is elastic and masses are unequal.
(ii) collision is inelastic but masses are unequal.
Select the correct alternative.
A particle of mass collides with a stationary particle and continues to move at an angle of with respect to the original direction. The second particle also recoils at an angle of to this direction. The mass of the second particle is (collision is elastic),
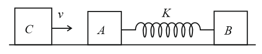
Two blocks and , each of mass ,are connected to a massless spring of natural length and spring constant . The blocks are initially resting on a smooth horizontal floor with the spring at its natural length as shown in the figure. A third identical block , also of mass , moves on the floor with speed along the line joining and and collides elastically with . Then,