B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: DPP 4.1
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: DPP 4.1
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: DPP 4.1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Mechanics - II JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: DPP 4.1 with Hints & Solutions
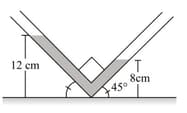
A U-tube in which the cross-sectional area of the limb on the left is one-quarter, the limb on the right contains mercury (density ). The level of mercury in the narrow limb is at a distance of from the upper end of the tube. What will be the rise in the level of mercury in the right limb if the left limb is filled to the top with water?
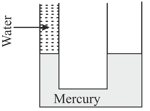
Two communicating vessels contain mercury. The diameter of one vessel is n times larger than the diameter of the other. A column of water of height h is poured into the left vessel. The mercury level will rise in the right-hand vessel (relative density of mercury and density of water) by
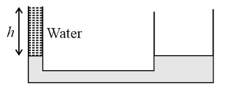
An L-shaped glass tube is kept inside a bus that is moving with constant acceleration. During the motion, the level of the liquid in the left arm is at whereas in the right arm, it is at when the orientation of the tube is as shown. Assuming that the diameter of the tube is much smaller than levels of the liquid and neglecting effect of surface tension, acceleration of the bus will be (.
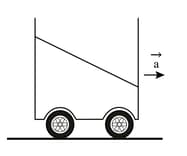
An open water tanker moving on a horizontal straight road has a cubical block of cork floating over its surface. If the tanker has an acceleration of as shown, the acceleration of the cork w.r.t. container is :
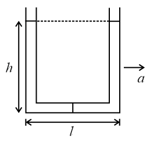
A -tube of base length filled with the same volume of two liquids of densities and is moving with an acceleration on the horizontal plane. If the height difference between the two surfaces (open to atmosphere) becomes zero, then the height is given by :
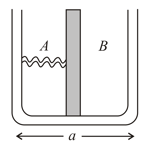
A broad vessel with a square base of edge is separated into two halves and by a smooth vertical piston. A spring of spring constant is filled across the compartment and the compartment is filled with water to a height Find the compression in the spring.
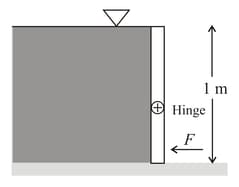
A rectangular gate stands vertical with water on one side of it hinged at the middle. The force required to the applied at the bottom to keep the gate in equilibrium is
Pressure is a scalar quantity because: