B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: DPP
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: DPP
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 1: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: DPP with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Optics and Modern Physics JEE Main & Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Ray Optics, Exercise 1: DPP with Hints & Solutions
As the position of an object reflected from a concave mirror is varied, the position of the image also varies. By letting change from to , the graph between versus will be,
The graph between and for a convex mirror is
A convergent beam of light is incident on a convex mirror to converge to a distance from the pole of the mirror. An inverted image of the same size is formed, coincident with the virtual object. What is the focal length of the mirror?
A thin rod of length is kept along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length such that its image is real and magnified and one end touches the rod. Its magnification will be
A square of side is placed at a distance of from a concave mirror of focal length . The centre of the square is at the axis of the mirror, and the plane is normal to the axis. The area enclosed by the image of the square is
A small piece of wire bent into an shape with upright and horizontal portions of equal lengths is placed with the horizontal portion along the axis of the concave mirror whose radius of curvature is . If the bend is from the pole of the mirror, then the ratio of the lengths of the images of the upright and horizontal portions of the wire is
A particle is moving towards a fixed convex mirror of focal length . The image also moves. If is equal to the speed of image and is equal to the speed of the object, then
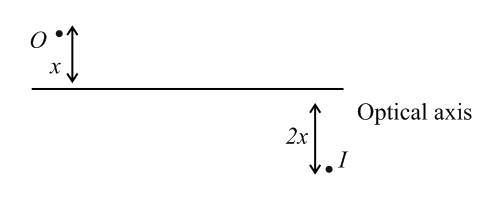
The positions of the object (real or virtual) and the image (real or virtual) with respect to the optical axis of a spherical mirror are shown. Then select the possible mirror and its position to realise it.